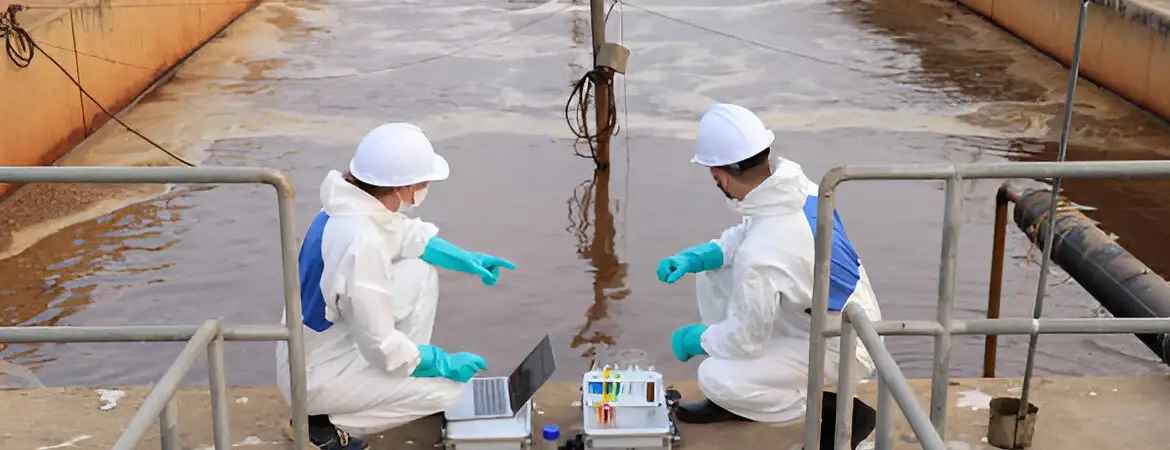
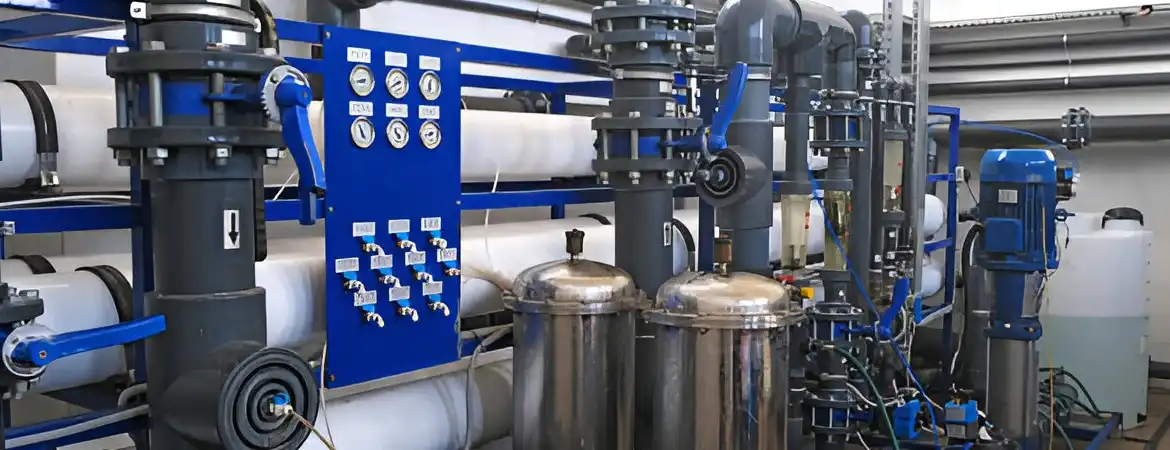
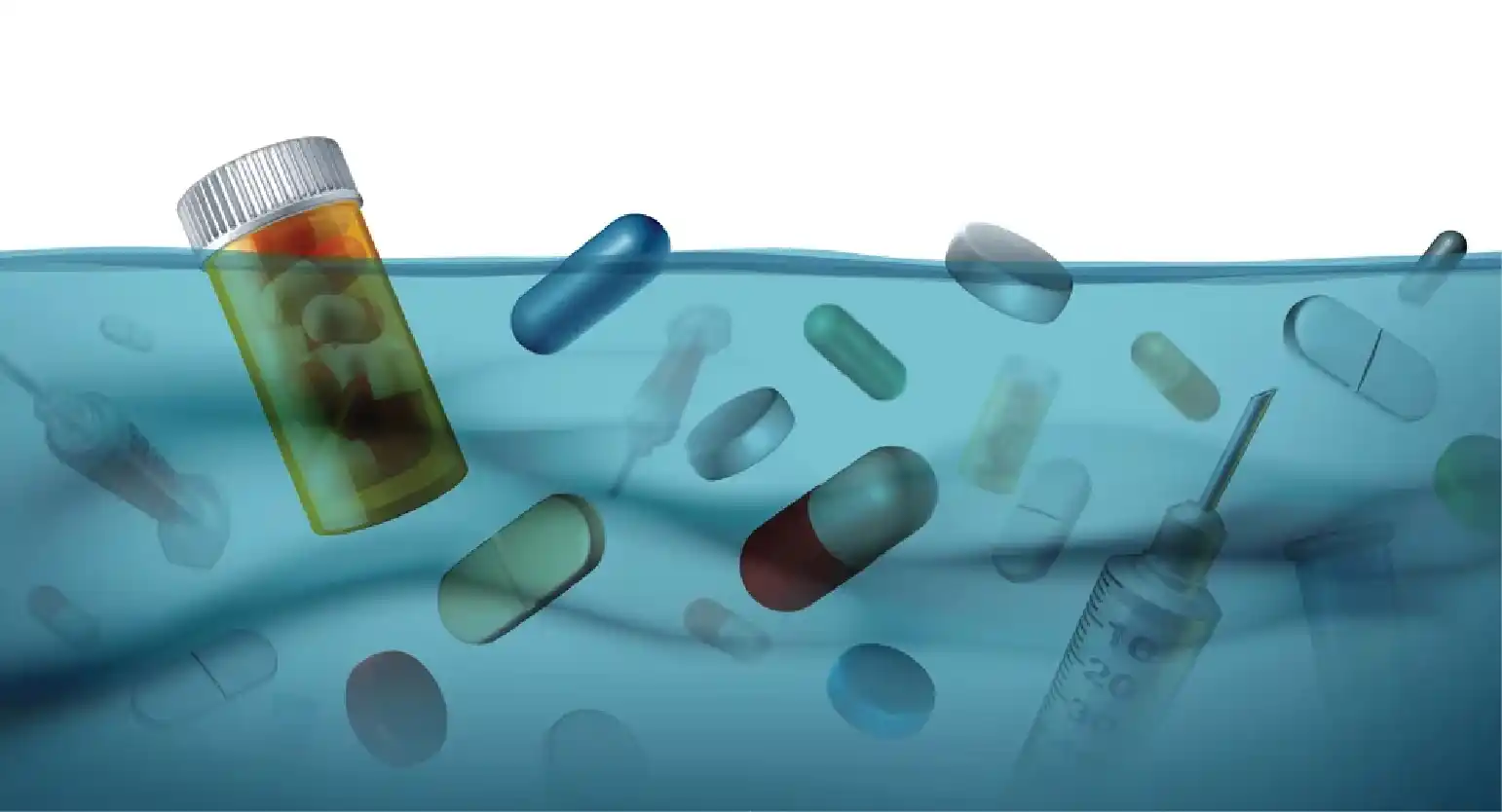
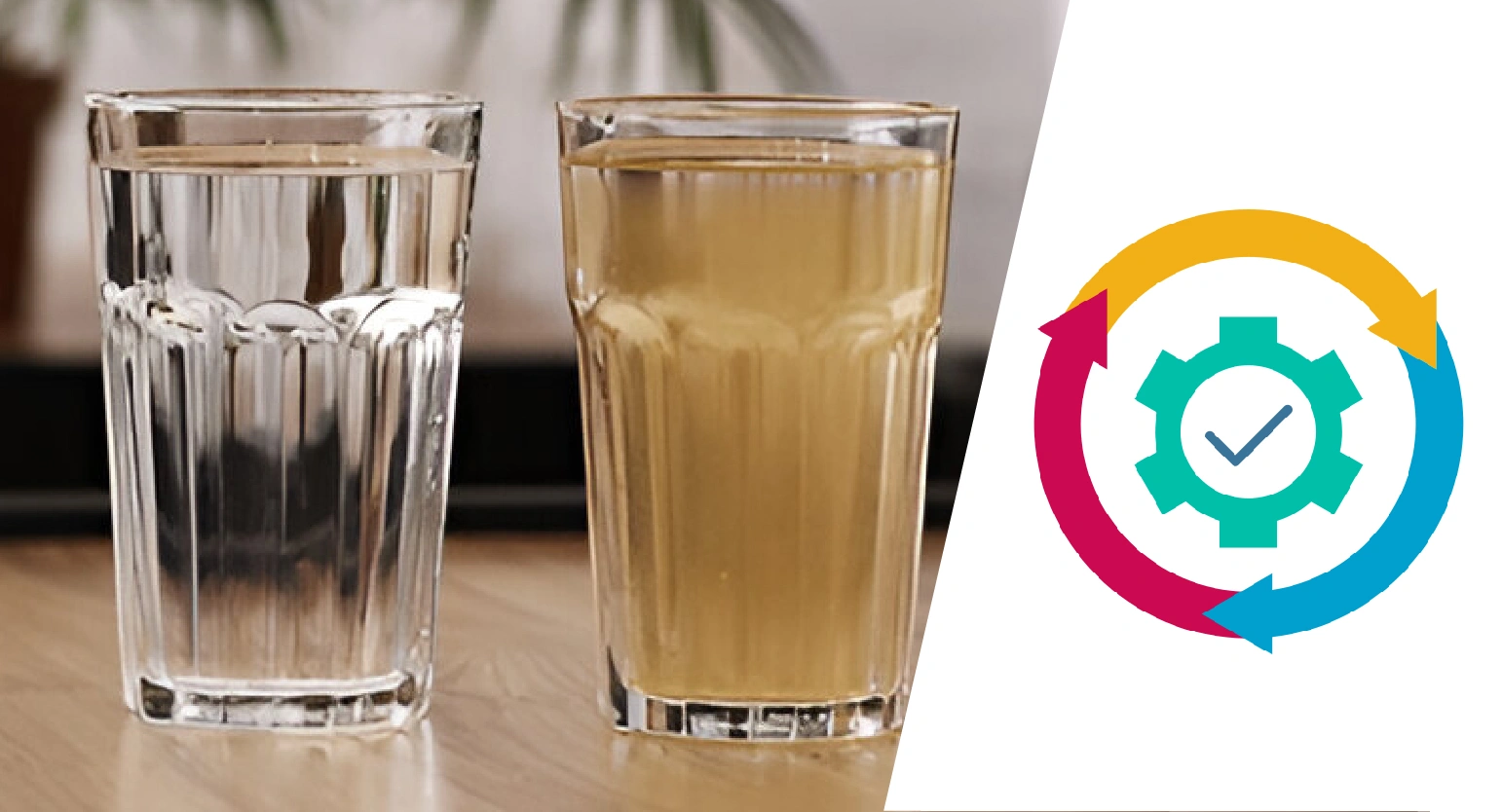
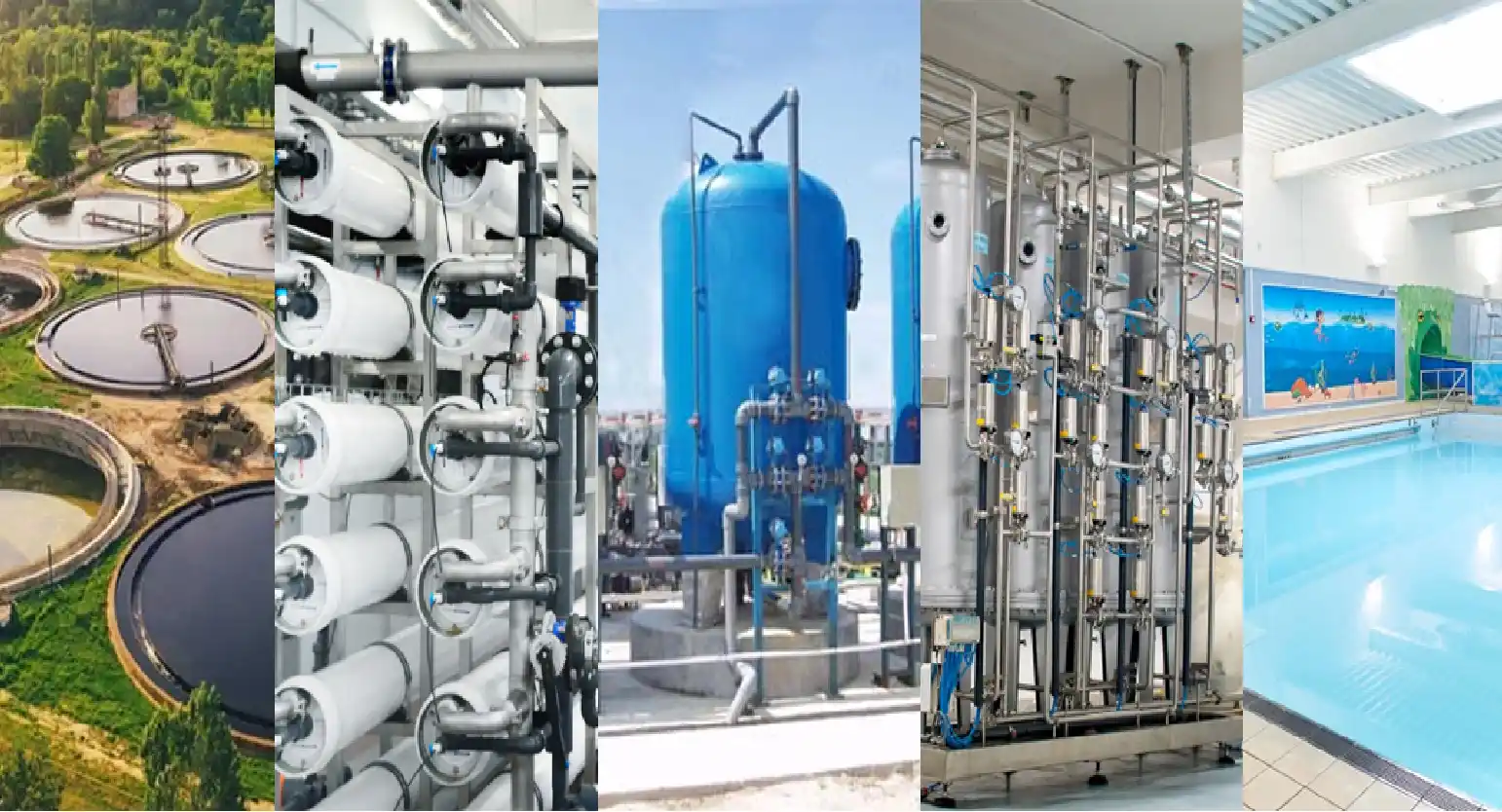
Water Softener Plant
Reverse Osmosis Plant
Drinking Water Treatment Plant
Zero Liquid Discharge Plant
Iron Removal Plant
DM Water Plant
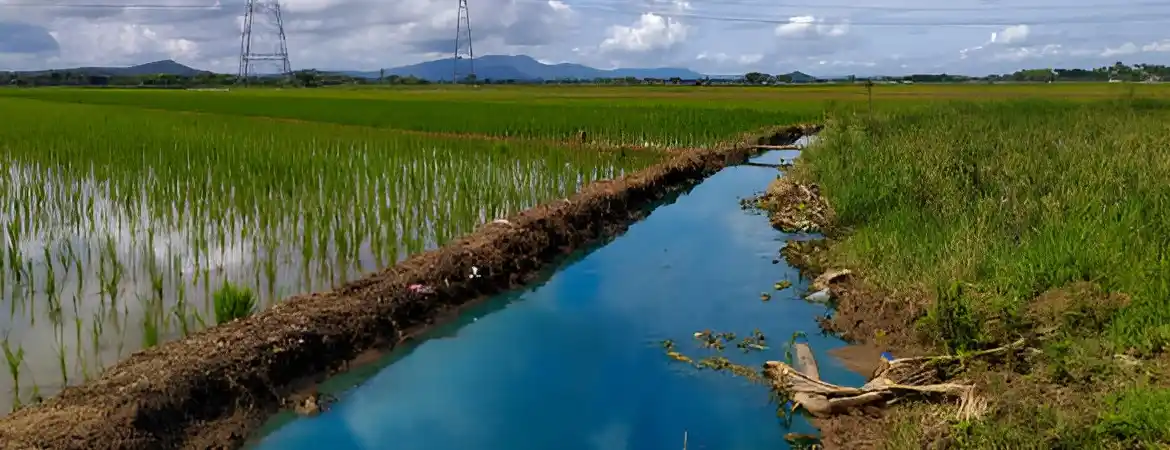
Rain Water Harvesting Plant
Domestic Purifier
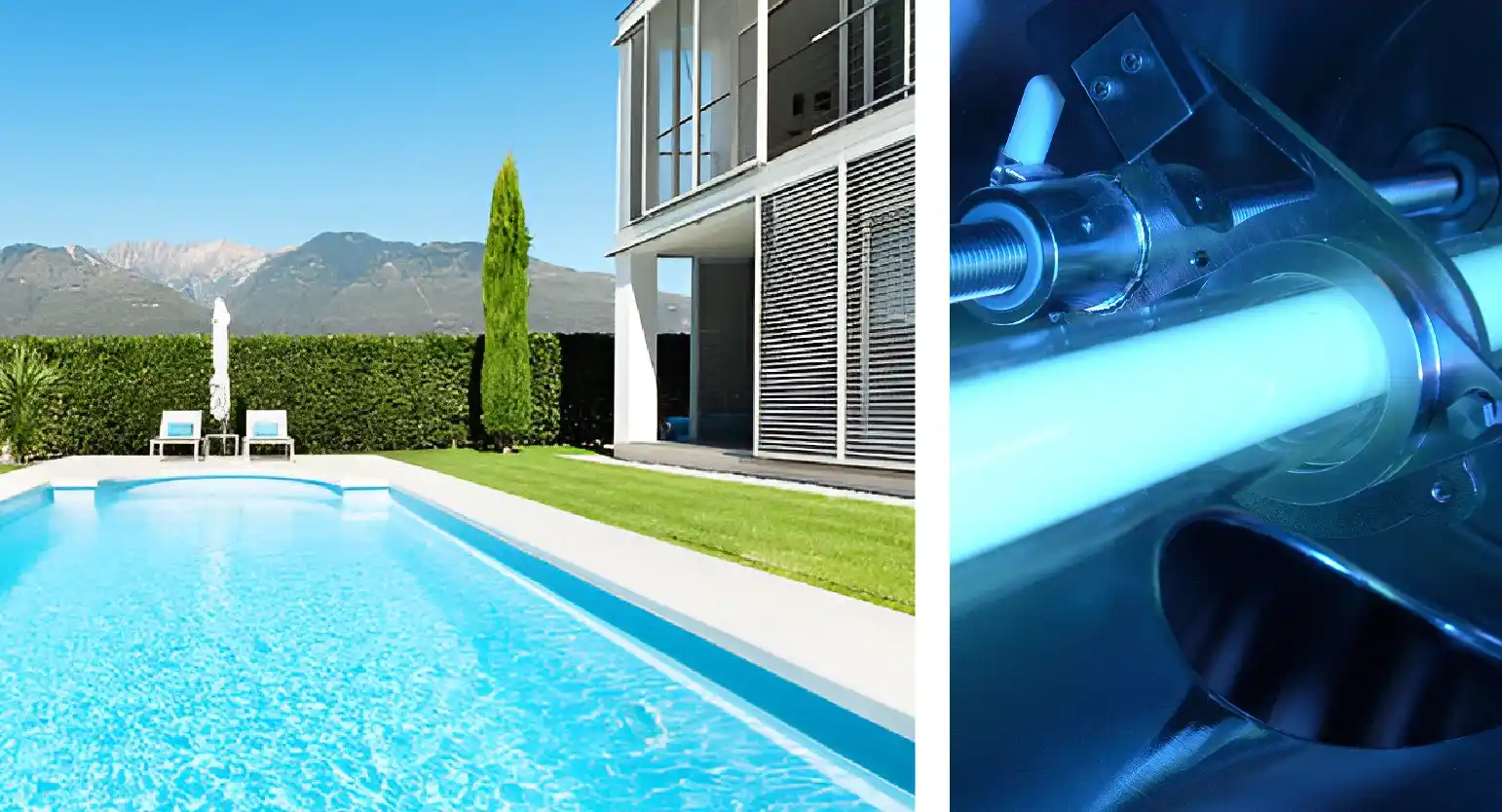
Swimming Pool Plant with Chemical
Pharmaceutical Treatment Plant
Desalination Plant
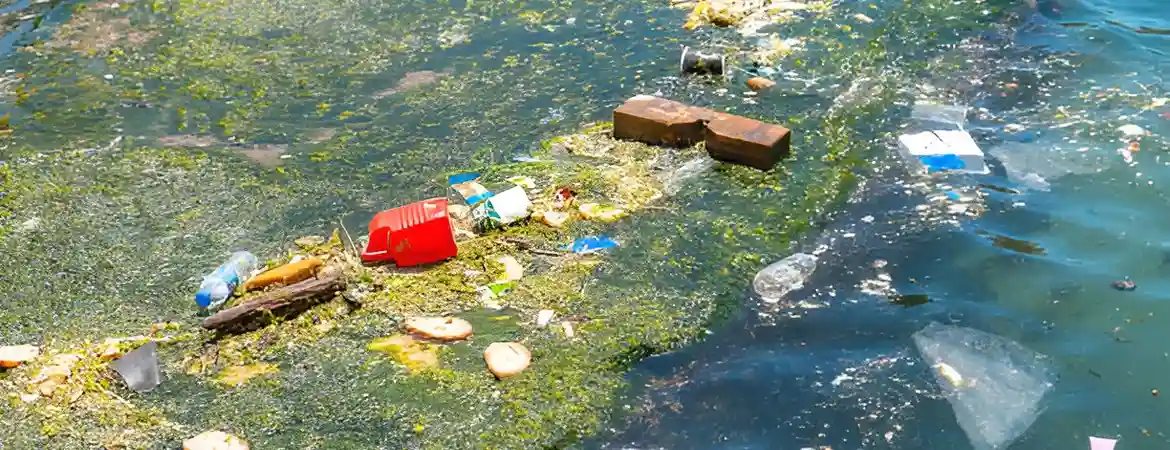
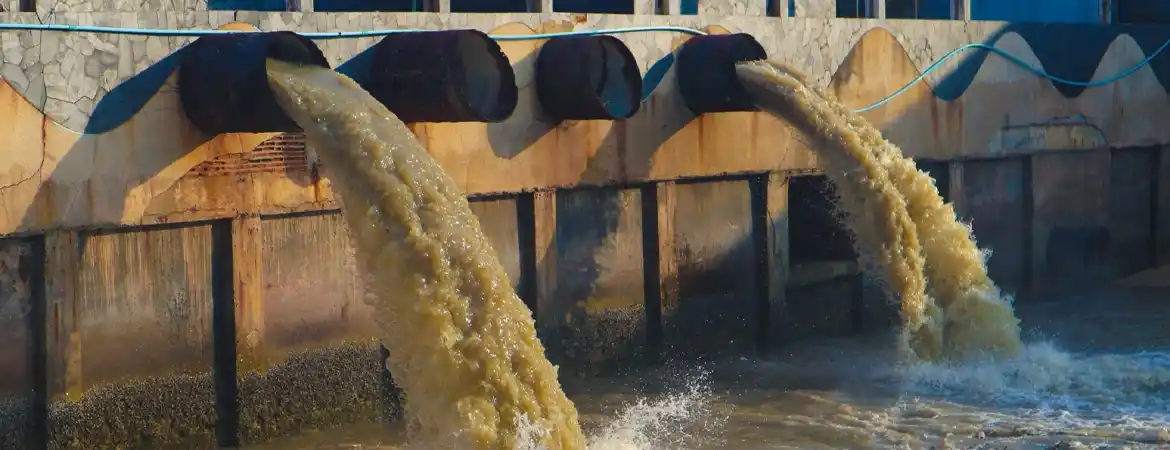
Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP)
Sewage Treatment Plant (STP)
Chlorine Reducer / Dechlorinator
Flocculent
Membrane Biocide
Membrane Cleaner
RO Antiscalant
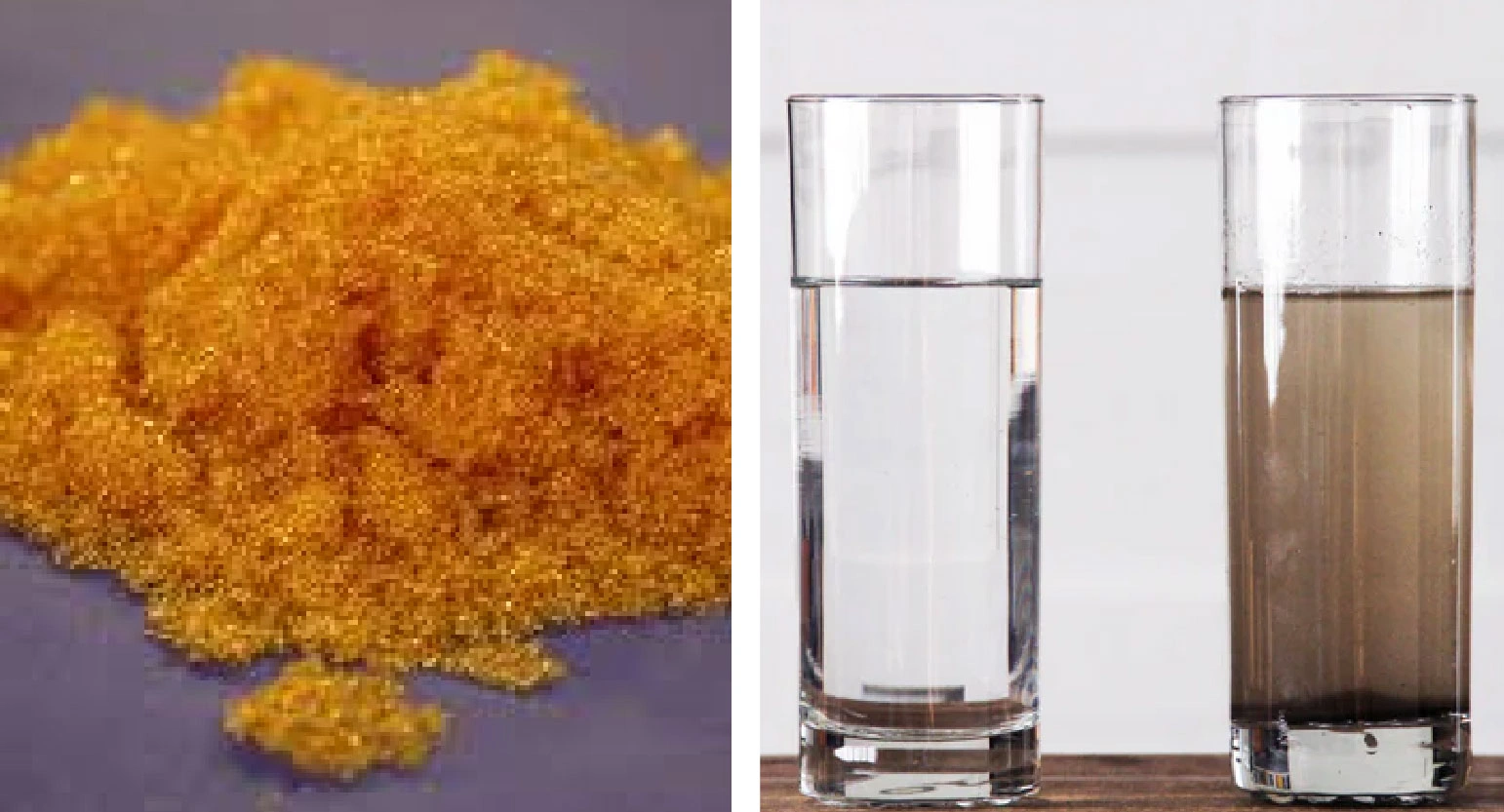
Ion Exchange Resin
Anthracite Filter Media
Activated Carbon
Iron Removal Media
Swimming Pool Chemical
Compact/Box type RO water purifier
Hot Cold Warm RO Purifier
Compact RO purifier
Economy RO Purifier
Filtran
Aqualin
Dow
Vontron
Tecoman
Karofi
Heron
kangaroo
Aquapro
Sanaky
Puricom
Pure Magic
Pristine
Aquafit
Logic Taiwan
Filtran
Micron Filter
Pentec
Eureka
Alkaline
Ecosoft
Pure Pro
Puran
Wilo
Raitapure
y series
deep well pump
BCST
Smart Measurement CO,. Ltd (SMC).
EMTEC
Trundean
Johnson
Filter Pipe
Aqua Taiwan
Green Aqua
Top Klean
Genesys RO
Purifina
In-Line
Easy Pure
UDF
Kemflo
Protech
Deluxe
korihome
Lan Shan
X-Treme
Maas Pure
Smart H2O
Tanklife
Hanna
Pentair
Kamranga
FRP
CNP Pump
Wellsys
KSU
Cascade
Deng Yuan
Livotech
Aquafit
Crystal Water
RFL
Flimtech
Toray
LEO Pump
Gazi Pump
Modina Pump
Extrepure Resin
Puretouch
Harmony
Puro Plus
Puroviet