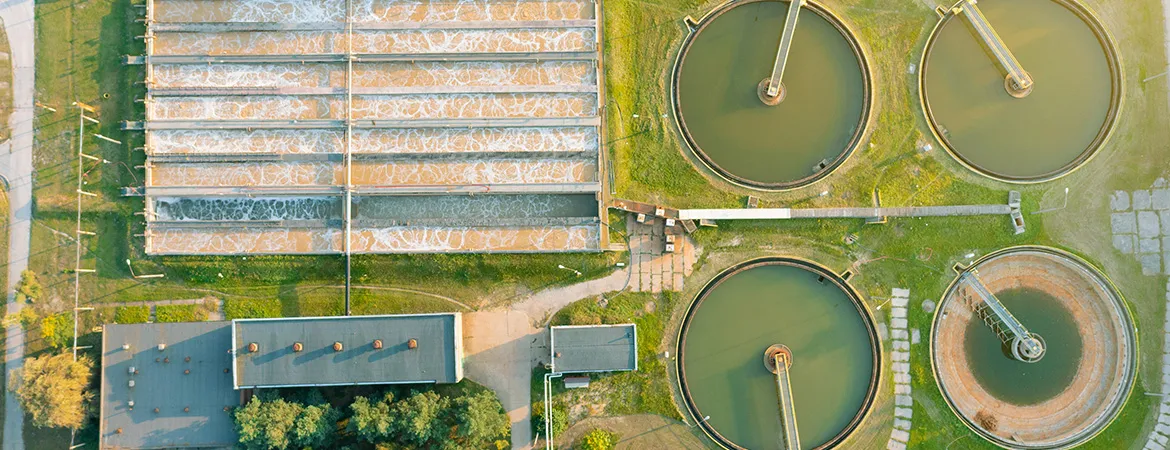
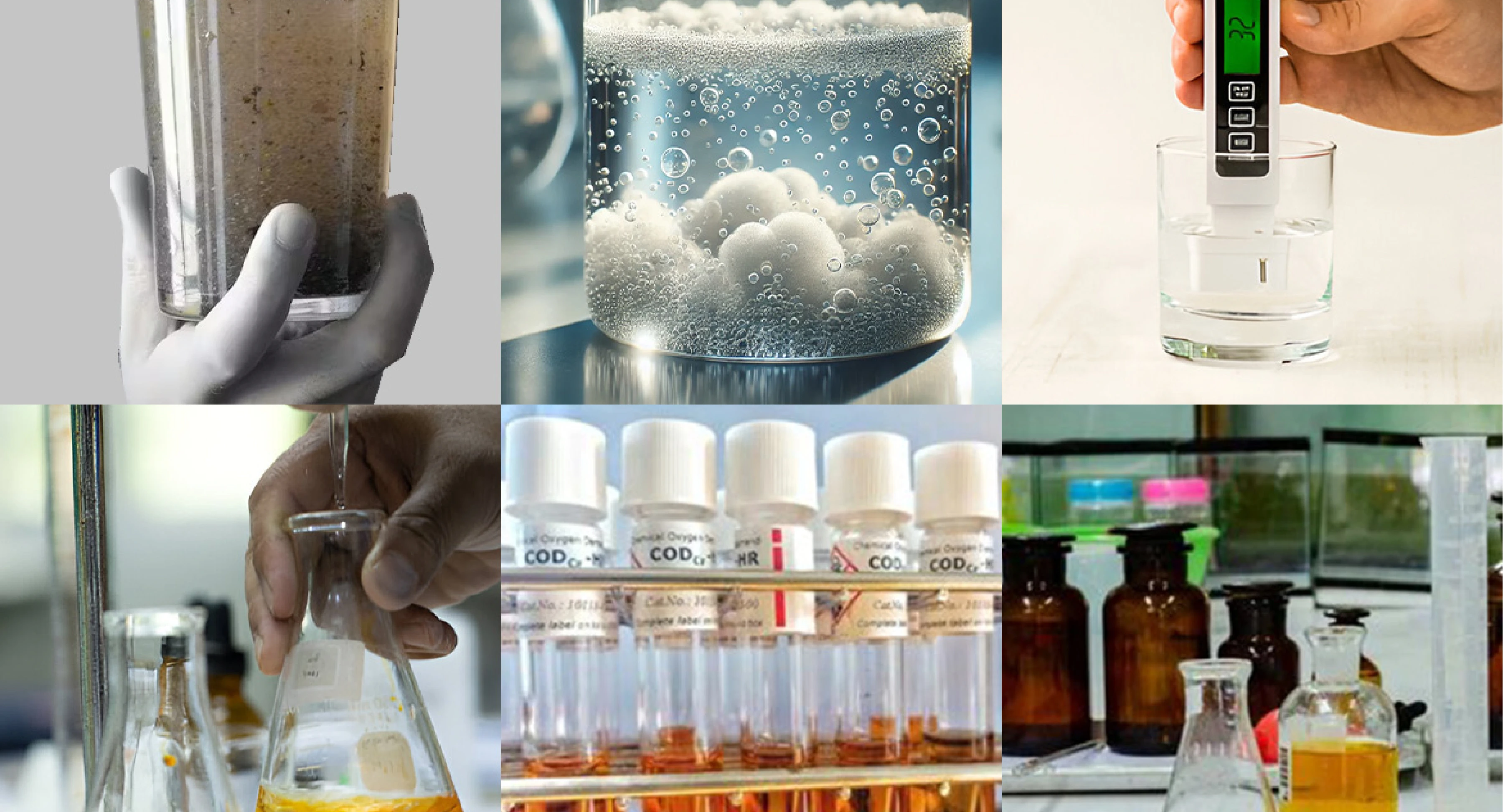
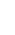Introduction
In
today's world, where industrial growth and environmental protection often seem
at odds, Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs) play a crucial role in bridging this
gap. These facilities are the unsung heroes of our modern industrial landscape,
working tirelessly to clean and purify wastewater before it's released back
into the environment. This blog post will delve into the world of ETPs,
exploring their importance, functions, and the various processes involved in
wastewater treatment.
What
is an Effluent Treatment Plant?
An
Effluent Treatment Plant, commonly known as an ETP, is a facility designed to
purify industrial wastewater and sewage before it's discharged into the
environment. These plants are essential for managing industrial effluent,
ensuring that harmful pollutants are removed or reduced to acceptable levels
before the water is released back into natural water bodies or municipal sewage
systems.
The
Importance of ETPs in Industrial Effluent Management
ETPs are
critical for several reasons:
- They help protect the
environment from harmful pollutants
- They ensure compliance with
environmental regulations
- They contribute to water
conservation efforts
- They help maintain public
health by preventing the spread of waterborne diseases
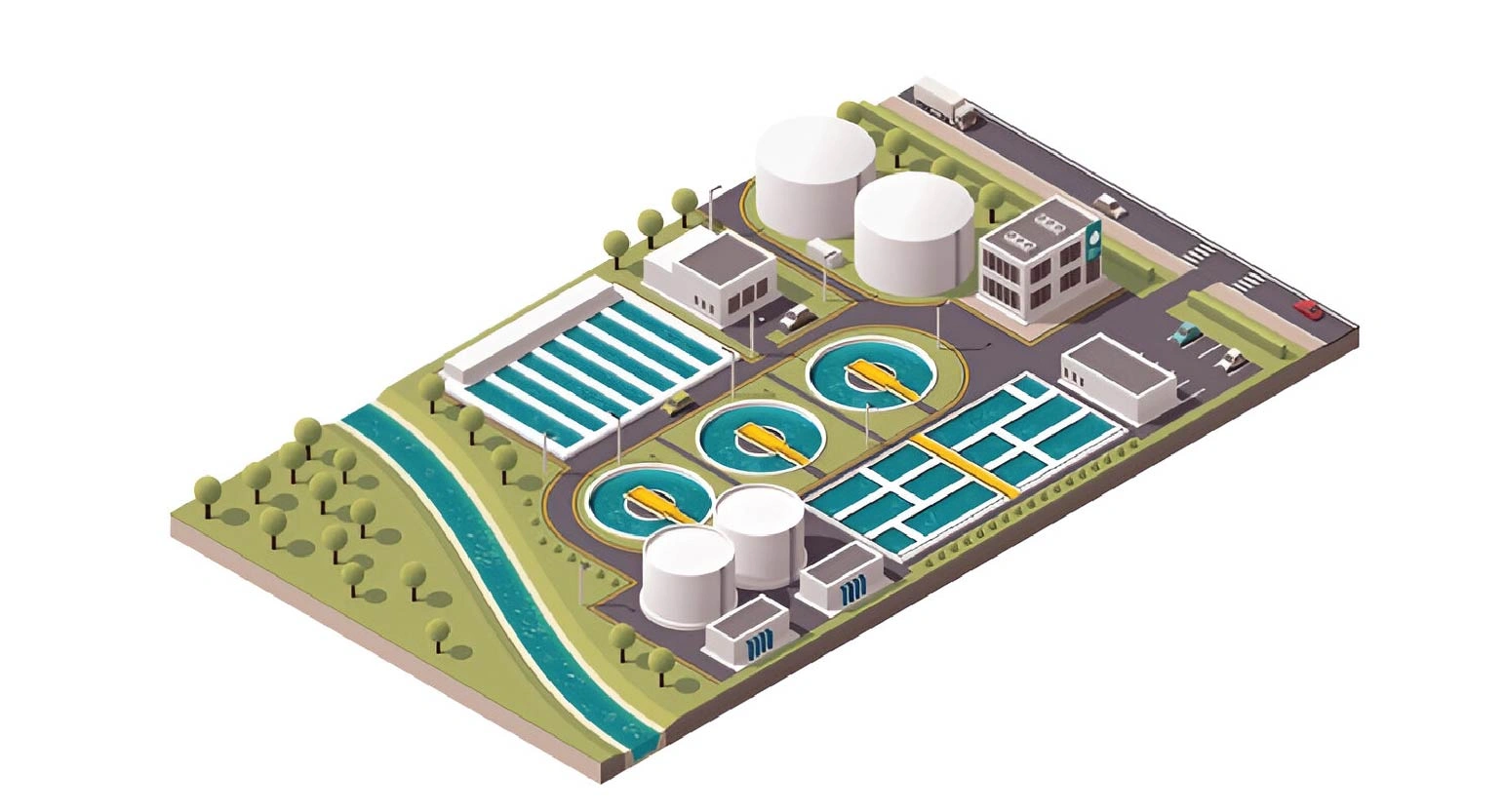
The Wastewater Treatment Process
The treatment of industrial effluent involves several stages, each designed to remove specific types of contaminants. Let's explore these stages in detail.
Primary Treatment
The first step in the wastewater treatment process focuses on removing solid materials from the effluent.
- Screening: Large debris is removed using screens or bars
- Sedimentation: Heavier particles settle to the bottom of tanks and are removed as sludge
- Oil and grease removal: Floating materials are skimmed off the surface
Secondary Treatment: Biological Processes
After primary treatment, the wastewater undergoes biological treatment to remove dissolved and suspended organic matter.
- Activated Sludge Process: Microorganisms break down organic pollutants
- Trickling Filters: Wastewater is sprayed over a bed of rocks or plastic media covered with microorganisms
- Anaerobic Digestion: Organic matter is broken down in the absence of oxygen
Tertiary Treatment: Advanced Purification
This stage involves advanced techniques to further purify the water:
- Chemical Treatment: Coagulants and flocculants are added to remove fine particles
- Filtration: Water passes through sand, gravel, or activated carbon filters
- Disinfection: Chlorine, UV light, or ozone is used to kill remaining pathogens
Chemical Treatment of Effluent
Chemical treatment plays a vital role in the ETP process, particularly in removing specific pollutants that biological processes can't effectively handle.
Common Chemicals Used in ETPs
- Coagulants: Aluminum sulfate, ferric chloride
- pH adjusters: Lime, sodium hydroxide, sulfuric acid
- Disinfectants: Chlorine, sodium hypochlorite
Benefits of Chemical Treatment
- Removes heavy metals and other toxic substances
- Adjusts pH levels to optimal ranges for biological treatment
- Enhances the efficiency of subsequent treatment processes
Sludge Management: A Critical Aspect of ETP Operation
Sludge, the solid residue produced during wastewater treatment, requires careful handling and disposal.
Sludge Treatment Methods
- Thickening: Reducing water content to decrease volume
- Stabilization: Reducing odors and pathogens
- Dewatering: Further reducing water content for easier handling
Sludge Disposal Options
- Land application as fertilizer (if safe)
- Incineration
- Landfill disposal (as a last resort)
ETP Design and Operation: Ensuring Optimal Performance
Designing and operating an effective ETP requires careful consideration of various factors:
- Wastewater characteristics
- Treatment objectives
- Local environmental regulations
- Available space and resources
Key Considerations in ETP Design
- Flexibility to handle varying effluent loads
- Energy efficiency
- Automation and process control
- Ease of maintenance and operation
Environmental Compliance in Wastewater Treatment
Meeting regulatory standards is a critical aspect of ETP operation. Environmental compliance officers and facility managers must stay up-to-date with:
- Local, state, and federal regulations
- Discharge permit requirements
- Monitoring and reporting obligations
Best Practices for Ensuring Compliance
- Regular monitoring and testing of effluent quality
- Proper record-keeping and documentation
- Staff training on compliance requirements
- Implementing a robust environmental management system
The Future of Wastewater Treatment
As technology advances and environmental concerns grow, the future of wastewater treatment looks promising:
- Membrane technologies for more efficient filtration
- Advanced oxidation processes for removing persistent pollutants
- Resource recovery from wastewater (e.g., energy, nutrients)
- Integration of artificial intelligence for process optimization
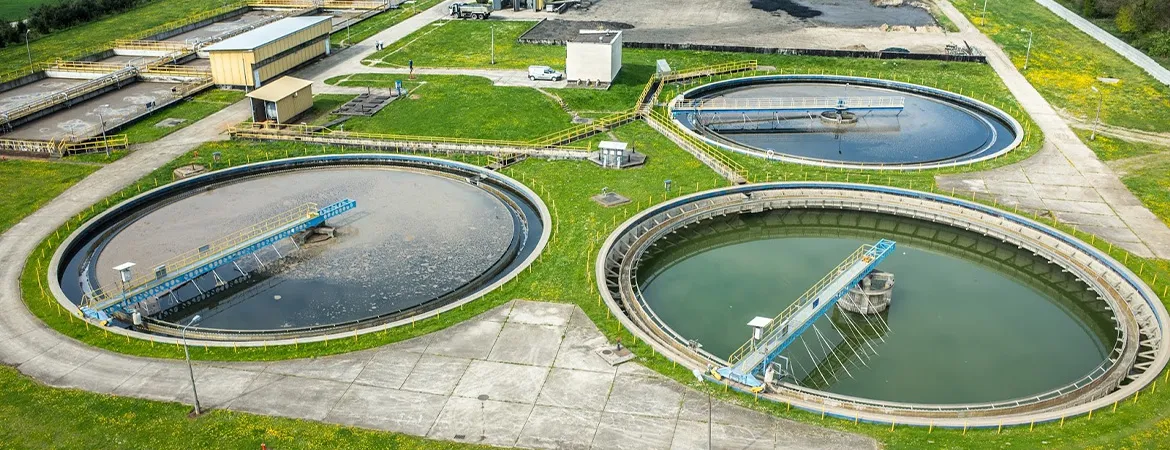

Biological ETP
Introduction
Biological Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP) are critical in managing and treating industrial wastewater, particularly for processes involving organic waste. These systems utilize biological processes to break down pollutants, ensuring that wastewater is treated to meet environmental standards before disposal or reuse. Aquafit Technology provides cutting-edge Biological ETP solutions, designed to handle a variety of industrial effluents efficiently.
Definition
A Biological Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) employs microorganisms to degrade organic pollutants in wastewater. The treatment relies on the natural metabolic processes of bacteria and other microbes to convert organic waste into less harmful substances, such as carbon dioxide and water. Biological ETPs are essential for industries that generate high volumes of organic wastewater, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and textiles.
Types of Biological ETP
- Activated Sludge Process:
- How It Works: This process involves aerating the wastewater in a tank to encourage the growth of microorganisms that consume organic pollutants. The treated water is then separated from the activated sludge, which is recycled back into the system.
- Applications: Widely used in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment due to its effectiveness in removing organic matter.
- Trickling Filter:
- How It Works: Wastewater is distributed over a bed of microbial-covered media, where microorganisms degrade organic matter as the water flows through.
- Applications: Suitable for small to medium-sized treatment facilities and industries with moderate organic waste loads.
- Sequential Batch Reactor (SBR):
- How It Works: This system treats wastewater in batches, allowing for different stages of treatment (e.g., aeration, settling) to occur in the same tank.
- Applications: Ideal for facilities with varying wastewater flows and loads.
Effects of Biological ETP
- Reduces Organic Load: Effectively decreases the concentration of organic pollutants in wastewater, reducing its environmental impact.
- Improves Water Quality: Treats wastewater to meet regulatory standards, ensuring that it is safe for discharge or reuse.
- Cost-Effective: Biological treatment processes are generally more economical compared to chemical or physical methods.
Conclusion
Biological ETPs are a vital component of modern wastewater management, providing an effective and sustainable solution for treating organic waste. These systems utilize natural processes to produce cleaner, safer effluents, benefiting both the environment and industry.
Aquafit Technology offers top-of-the-line Biological ETP solutions tailored to your specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with environmental standards. Trust us to deliver the best in biological wastewater treatment technology.
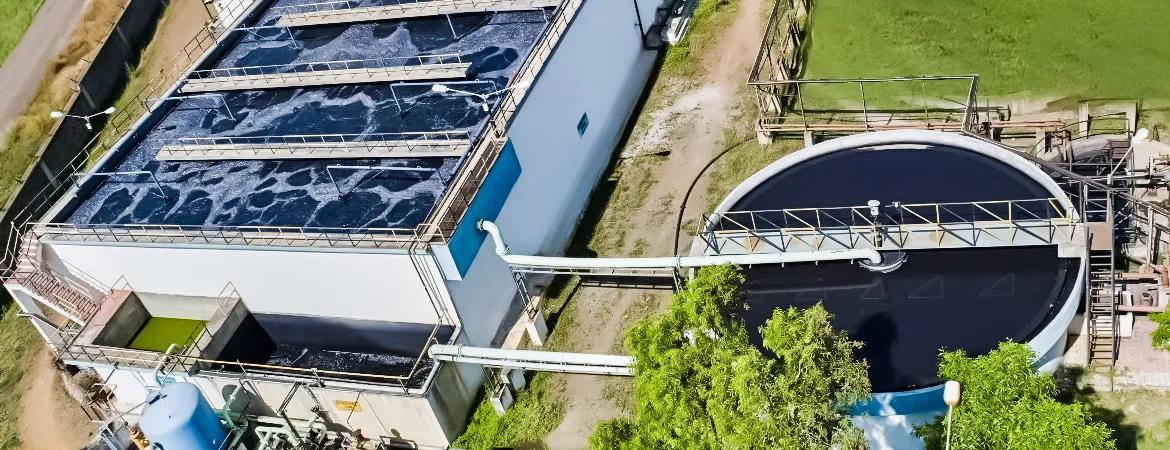

Biochemical
ETP
Introduction
Biochemical
Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP) are specialized systems designed to treat
industrial wastewater through biochemical processes. These plants leverage the
natural ability of microorganisms to break down organic pollutants, ensuring
that wastewater is treated effectively to meet environmental regulations.
Aquafit Technology offers advanced Biochemical ETP solutions, tailored to meet
the diverse needs of industries in Bangladesh.
Definition
Biochemical
Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP) utilize biochemical reactions to decompose organic
contaminants in wastewater. This method harnesses the activity of bacteria and
other microorganisms to convert complex organic substances into simpler, less
harmful compounds like carbon dioxide and water. Biochemical ETPs are
particularly effective for industries with high organic waste content, such as
food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing.
Types
of Biochemical ETP
- Activated Sludge
Process:
- How It Works: This process
involves aerating wastewater in a large tank to promote the growth of
microorganisms. These microbes consume organic pollutants, which are then
separated from the treated water.
- Applications: Commonly used for
treating municipal and industrial wastewater due to its efficiency in
removing organic matter.
- Rotating Biological
Contactors (RBC):
- How It Works: Wastewater is
passed over rotating discs coated with a microbial biofilm. As the discs
rotate, microorganisms break down organic pollutants from the wastewater.
- Applications: Suitable for
small to medium-sized treatment plants, providing efficient treatment
with lower energy consumption.
- Moving Bed Biofilm
Reactor (MBBR):
- How It Works: This system uses
plastic carriers that support a biofilm of microorganisms. Wastewater
flows through the reactor, and the biofilm degrades organic matter.
- Applications: Ideal for
facilities with fluctuating wastewater loads and where space is limited.
Effects
of Biochemical ETP
- Reduces Organic
Load:
Effectively lowers the concentration of organic contaminants, making the
wastewater safer for discharge or reuse.
- Enhances Water
Quality:
Produces treated water that meets regulatory standards, helping industries
comply with environmental regulations.
- Cost-Effective and
Sustainable:
Biochemical treatment processes are generally more economical and
environmentally friendly compared to chemical alternatives.
Conclusion
Biochemical
ETPs offer an effective and sustainable solution for treating industrial
wastewater, utilizing natural biological processes to ensure high-quality
effluents. These systems are essential for industries that produce high volumes
of organic waste, providing both environmental and economic benefits.
Aquafit
Technology provides state-of-the-art Biochemical ETP systems, designed to meet
the specific needs of various industries in Bangladesh. Trust us to deliver the
best in biochemical wastewater treatment technology, ensuring your operations
are both efficient and compliant with environmental standards.
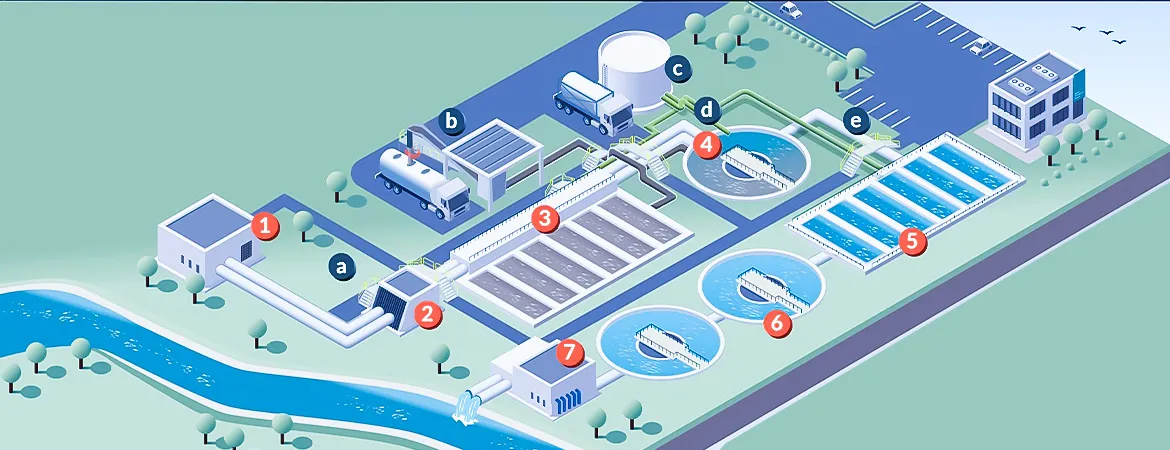
MBBR
Technology
Introduction
Moving
Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) technology is a cutting-edge solution for wastewater
treatment that offers enhanced efficiency and flexibility. This technology
leverages the natural processes of microorganisms to degrade organic
contaminants, making it an ideal choice for a range of industrial and municipal
applications. Aquafit Technology provides state-of-the-art MBBR systems,
tailored to meet the specific needs of wastewater treatment in Bangladesh.
Definition
Moving
Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)
is a biological wastewater treatment technology that uses suspended plastic
carriers to support the growth of a biofilm of microorganisms. These
microorganisms break down organic pollutants as wastewater flows through the
reactor. MBBR systems combine the benefits of both activated sludge and biofilm
technologies, providing a highly efficient and compact treatment solution.
How
MBBR Technology Works
- Plastic Carriers: The MBBR system
contains plastic media with high surface area, which provides a habitat
for microorganisms to grow. These carriers are kept in constant motion by
aeration or mixing, ensuring that the biofilm remains active and
effective.
- Biological
Treatment:
As wastewater flows through the reactor, the microorganisms on the plastic
carriers metabolize organic pollutants, converting them into simpler
compounds such as carbon dioxide and water.
- Separation: After treatment,
the water is separated from the biomass. The treated effluent is typically
of high quality, meeting regulatory standards for discharge or reuse.
Types
of MBBR Systems
- Single-Stage MBBR: Used for
straightforward applications where primary and secondary treatment occur
in the same reactor, ideal for smaller facilities or less complex
wastewater.
- Two-Stage MBBR: Involves separate
reactors for primary and secondary treatment, providing greater
flexibility and efficiency for handling varying wastewater loads and
compositions.
Benefits
of MBBR Technology
- High Efficiency: MBBR systems offer
high treatment efficiency, effectively removing organic contaminants and
improving water quality.
- Compact Design: The use of plastic
carriers allows for a smaller footprint compared to traditional treatment
methods, making MBBR systems suitable for facilities with limited space.
- Flexible Operation: MBBR technology
can easily adapt to changes in wastewater flow and composition, offering a
scalable solution for various applications.
- Low Maintenance: MBBR systems
require minimal maintenance, with the plastic carriers providing a durable
and long-lasting support structure for the biofilm.
Conclusion
MBBR
technology is an advanced and versatile solution for wastewater treatment,
combining the benefits of biofilm and activated sludge processes. Its high
efficiency, compact design, and flexibility make it an excellent choice for a
wide range of applications.
Aquafit
Technology offers cutting-edge MBBR systems tailored to meet the specific needs
of wastewater treatment in Bangladesh. Our solutions ensure optimal performance
and compliance with environmental standards, helping you achieve the highest
quality treated water.
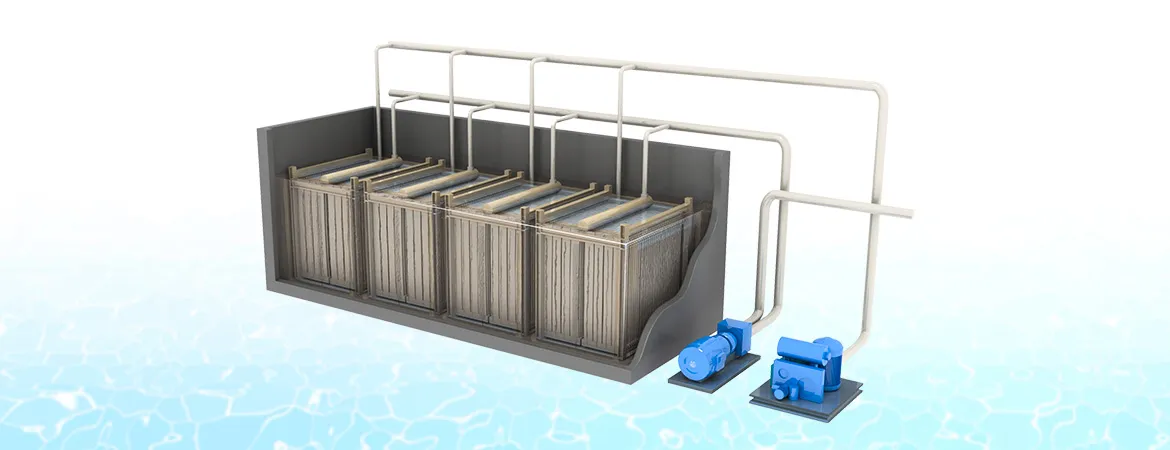

MBR
Technology
Introduction
Membrane
Bioreactor (MBR) technology is at the forefront of wastewater treatment
innovation, combining biological treatment processes with membrane filtration
to achieve superior water quality. MBR systems are known for their high
efficiency, compact footprint, and ability to produce high-quality effluent.
Aquafit Technology offers advanced MBR solutions, designed to meet the
demanding requirements of wastewater treatment in Bangladesh.
Definition
Membrane
Bioreactor (MBR)
technology integrates biological treatment processes with membrane filtration
to simultaneously remove organic pollutants and separate solids from
wastewater. The system uses a combination of activated sludge and membrane
filtration to achieve high-quality treated water that meets or exceeds
regulatory standards.
How
MBR Technology Works
- Biological
Treatment:
Wastewater is first treated biologically using activated sludge, where
microorganisms break down organic contaminants. This process occurs in a
bioreactor tank.
- Membrane
Filtration:
After biological treatment, the mixed liquor (a mixture of treated water
and microorganisms) passes through a membrane filtration unit. The
membranes, typically made from materials like polyvinylidene fluoride
(PVDF) or ceramic, filter out suspended solids, bacteria, and other
contaminants, producing a clear and high-quality effluent.
- Effluent Quality: The treated water,
or permeate, is of high quality and can be safely discharged or reused for
various applications, including industrial processes, irrigation, and even
potable use in some cases.
Types
of MBR Systems
- Submerged Membrane
Bioreactors:
In this system, membranes are immersed directly in the bioreactor tank.
The mixed liquor flows through the membranes for filtration, and the clean
permeate is collected.
- External Membrane
Bioreactors:
Here, membranes are located outside the bioreactor tank. The mixed liquor
is pumped through the membrane module for filtration before returning to
the bioreactor.
Benefits
of MBR Technology
- High-Quality
Effluent:
MBR systems produce effluent with very low levels of suspended solids and
contaminants, making it suitable for discharge or reuse in sensitive
environments.
- Compact Design: The integration of
biological treatment with membrane filtration allows MBR systems to have a
smaller footprint compared to traditional treatment methods, making them
ideal for facilities with space constraints.
- Reduced Sludge
Production:
MBR technology reduces the volume of excess sludge generated, leading to
lower disposal costs and improved operational efficiency.
- Flexibility and
Scalability:
MBR systems can be easily scaled to accommodate varying wastewater flows
and treatment requirements, providing a versatile solution for diverse
applications.
Conclusion
MBR
technology represents a significant advancement in wastewater treatment,
offering high efficiency, compact design, and exceptional effluent quality. Its
ability to integrate biological and filtration processes makes it an ideal
choice for applications where superior water quality is essential.
Aquafit
Technology provides state-of-the-art MBR systems tailored to the specific needs
of wastewater treatment in Bangladesh. Our solutions ensure optimal performance
and compliance with environmental standards, helping you achieve the highest
quality treated water.
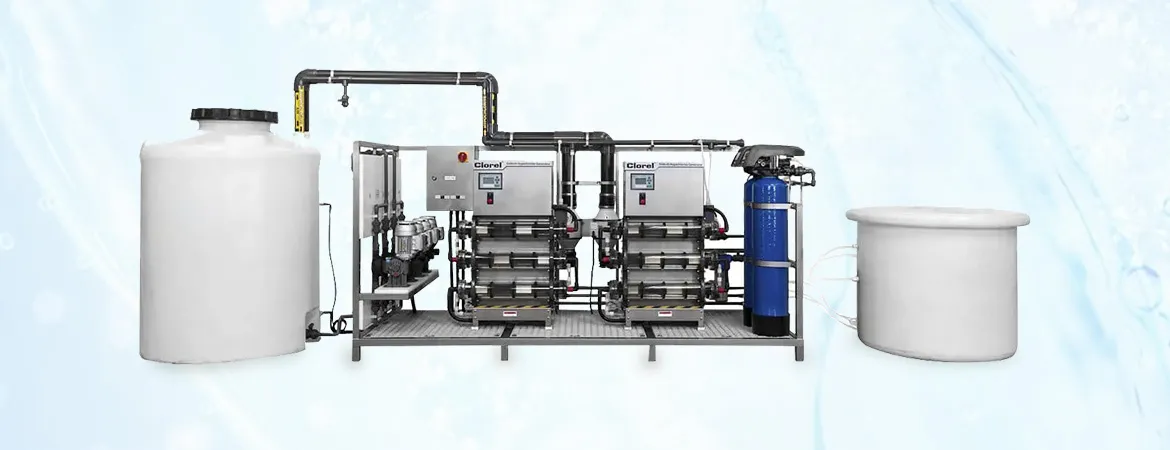

Electrolysis
Technology
Introduction
Electrolysis
technology is a transformative process used in various industries for water
treatment, purification, and disinfection. By applying electrical current to
water, electrolysis facilitates the breakdown of contaminants and the
generation of useful byproducts, making it an efficient and versatile
technology. Aquafit Technology offers advanced electrolysis solutions, designed
to meet the specific needs of water treatment in Bangladesh.
Definition
Electrolysis is a chemical process
that uses electrical current to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. In
the context of water treatment, electrolysis involves passing an electric
current through water to produce various beneficial effects, including the generation
of disinfecting agents and the removal of contaminants.
How
Electrolysis Technology Works
- Electrolytic Cells: Water is placed in
an electrolytic cell, which contains two electrodes—an anode and a
cathode. When an electrical current is applied, it causes a chemical
reaction at the electrodes.
- Production of
Disinfectants:
At the anode, water undergoes oxidation to produce chlorine, ozone, or
other disinfecting agents. These substances effectively kill bacteria,
viruses, and other microorganisms. At the cathode, reduction reactions may
occur, which can help remove contaminants from the water.
- Contaminant
Removal:
Electrolysis can break down organic contaminants, precipitate heavy
metals, and assist in the removal of impurities, resulting in cleaner and
safer water.
Types
of Electrolysis Systems
- Chlorine Generation
Systems:
- How It Works: Chlorine is
produced at the anode, which is then used for disinfecting water. This
method is commonly employed in water treatment plants for municipal and
industrial applications.
- Ozone Generation
Systems:
- How It Works: Ozone is
generated from oxygen and used as a powerful disinfectant and oxidizing
agent. Ozone systems are effective in removing organic contaminants and
improving water quality.
- Electrocoagulation
Systems:
- How It Works:
Electrocoagulation uses electrical current to induce coagulation and
flocculation processes, which help in the removal of suspended solids,
heavy metals, and other pollutants.
Benefits
of Electrolysis Technology
- Effective
Disinfection:
Electrolysis generates powerful disinfecting agents like chlorine and
ozone, which effectively kill microorganisms and purify water.
- Environmentally
Friendly:
Electrolysis does not produce harmful byproducts, making it a clean and
sustainable solution for water treatment.
- Versatile
Applications:
Electrolysis can be used for a range of applications, including municipal
water treatment, industrial processes, and wastewater treatment.
- Cost-Effective: With minimal
chemical requirements and low operational costs, electrolysis technology
offers an economical solution for maintaining high water quality.
Conclusion
Electrolysis
technology represents a significant advancement in water treatment, offering
effective disinfection, contaminant removal, and environmentally friendly
solutions. Its versatility and efficiency make it an ideal choice for a wide
range of applications.
Aquafit
Technology provides state-of-the-art electrolysis systems tailored to the
specific needs of water treatment in Bangladesh. Our solutions ensure optimal
performance and compliance with environmental standards, helping you achieve
the highest quality water.

Zero
Liquid Discharge (ZLD) Plants for ETP
Introduction
Zero
Liquid Discharge (ZLD) plants are advanced systems designed to treat and reuse
wastewater, achieving a state where no liquid waste is discharged into the environment.
In the context of Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP), ZLD technology plays a
crucial role in maximizing water reuse and minimizing environmental impact.
Aquafit Technology provides cutting-edge ZLD solutions tailored to enhance the
sustainability and efficiency of wastewater treatment processes in Bangladesh.
Definition
Zero
Liquid Discharge (ZLD)
refers to a wastewater management process where all the treated water is
recovered and reused, and no liquid waste is discharged into the environment.
This approach involves the complete treatment and recycling of wastewater,
ensuring that only solid residues are left behind, which can often be further
processed or disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner.
How
ZLD Plants Work
- Pre-Treatment: The wastewater
from ETP is first subjected to pre-treatment processes to remove larger
solids and contaminants. This step often includes filtration,
sedimentation, and chemical dosing.
- Advanced Treatment: Following
pre-treatment, advanced technologies such as Reverse Osmosis (RO),
Electrodialysis (ED), and Evaporation are used to further purify the
water. These methods concentrate contaminants and recover high-quality
water.
- Concentration and
Crystallization:
The concentrated waste from the advanced treatment processes is then
subjected to evaporation or crystallization. This step converts the
concentrated waste into solid residues and pure water.
- Water Reuse: The purified water
recovered from the ZLD process is reused within the industrial facility
for various applications, such as cooling, cleaning, and other processes.
This reduces the need for fresh water and minimizes wastewater disposal.
Benefits
of ZLD Plants
- Environmental
Protection:
ZLD plants eliminate liquid waste discharge, significantly reducing the
environmental impact and contributing to pollution prevention.
- Resource
Efficiency:
By recovering and reusing treated water, ZLD systems reduce the demand for
fresh water resources, enhancing overall resource efficiency.
- Regulatory
Compliance:
ZLD technology helps industries meet stringent environmental regulations
and discharge standards, avoiding potential fines and penalties.
- Cost Savings: Although the
initial investment in ZLD technology can be high, long-term savings are
achieved through reduced water procurement costs and minimized waste
disposal expenses.
Conclusion
Zero
Liquid Discharge (ZLD) plants represent a significant advancement in wastewater
management, offering a sustainable solution for treating and reusing
ETP-treated water. By recovering and reusing virtually all treated water, ZLD
systems contribute to environmental protection and resource efficiency.
Aquafit
Technology provides state-of-the-art ZLD solutions designed to optimize
wastewater reuse and enhance sustainability. Our expertise ensures that your
ETP-treated water is managed efficiently, helping you achieve zero liquid
discharge and meet your environmental goals.
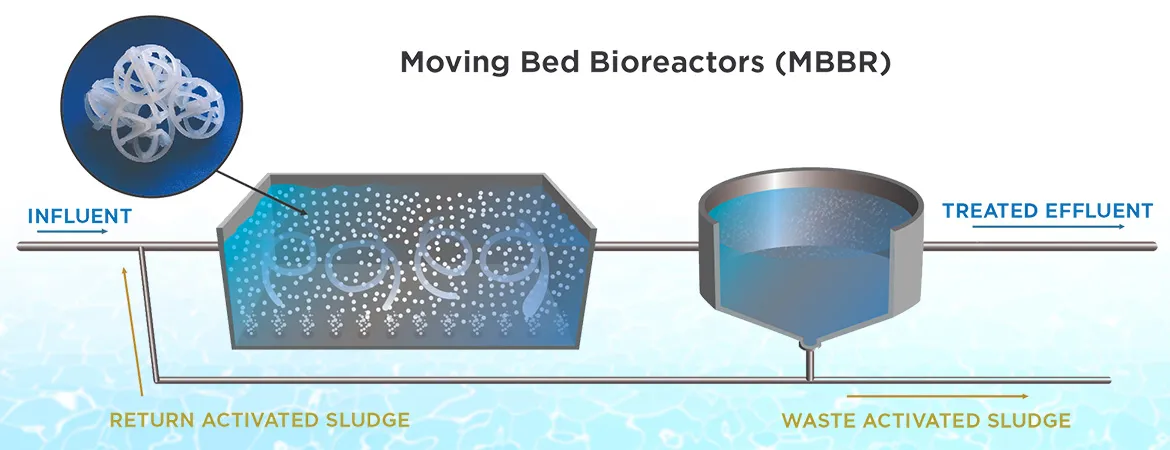
RO,
UF, and UV Technologies for Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP)
Introduction
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) are essential for managing and treating industrial
wastewater, ensuring that it meets environmental standards before discharge or
reuse. Among the advanced technologies used in ETPs, Reverse Osmosis (RO),
Ultrafiltration (UF), and Ultraviolet (UV) disinfection play crucial roles in
achieving high-quality treated water. Aquafit Technology offers
state-of-the-art solutions integrating RO, UF, and UV technologies to enhance
the effectiveness of wastewater treatment processes in Bangladesh.
Reverse
Osmosis (RO)
Definition: Reverse Osmosis (RO) is
a filtration process that uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove contaminants
from water. Under high pressure, water is forced through the membrane, which
retains dissolved solids, organic compounds, and other impurities, allowing
only clean water to pass through.
How
It Works:
- High Pressure: Water is
pressurized to overcome the natural osmotic pressure, forcing it through
the RO membrane.
- Contaminant
Removal:
The membrane filters out contaminants including salts, metals, and organic
compounds, producing purified water.
Benefits:
- High Purity: RO effectively
removes a wide range of contaminants, ensuring high-quality treated water.
- Versatile: Suitable for
various applications, including industrial processes and potable water
production.
- Efficient: Reduces the need
for chemical treatments and minimizes waste production.
Ultrafiltration
(UF)
Definition: Ultrafiltration (UF) is
a membrane filtration process that separates suspended solids, colloids, and
macromolecules from water. UF membranes have larger pore sizes compared to RO
membranes, allowing them to filter out larger particles while permitting water
and smaller molecules to pass through.
How
It Works:
- Membrane
Filtration:
Water flows through the UF membrane, which retains particles and
contaminants larger than the membrane’s pore size.
- Filtrate
Collection:
Clean water, free from larger impurities, is collected as the permeate.
Benefits:
- Effective Filtration: UF removes
suspended solids, bacteria, and some viruses, producing clean water with
minimal fouling.
- Low Energy
Consumption:
Requires less pressure than RO, leading to lower operational costs.
- Pre-Treatment: Often used as a
pre-treatment for RO systems to reduce membrane fouling and extend
membrane life.
Ultraviolet
(UV) Disinfection
Definition: Ultraviolet (UV)
disinfection is a water treatment process that uses UV light to kill or
inactivate microorganisms. UV light disrupts the DNA of bacteria, viruses, and
other pathogens, rendering them unable to reproduce and cause harm.
How
It Works:
- UV Exposure: Water flows
through a UV chamber where it is exposed to UV light.
- Microbial
Inactivation:
The UV light penetrates the cells of microorganisms, causing DNA damage
and inactivating them.
Benefits:
- Effective
Disinfection:
UV technology provides a chemical-free method to kill pathogens, ensuring
safe water.
- Immediate Action: Offers rapid
disinfection with no residual effects or byproducts.
- Low Maintenance: Requires minimal
maintenance and operating costs compared to chemical disinfection methods.
Conclusion
Integrating
RO, UF, and UV technologies in Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP) enhances the
effectiveness of wastewater treatment, ensuring high-quality, safe, and
compliant water. Each technology offers unique benefits, from high purity and
effective filtration to reliable disinfection.
Aquafit
Technology provides advanced RO, UF, and UV solutions tailored to your specific
wastewater treatment needs. Our expertise ensures optimal performance and
compliance with environmental standards, helping you achieve the highest
quality treated water.
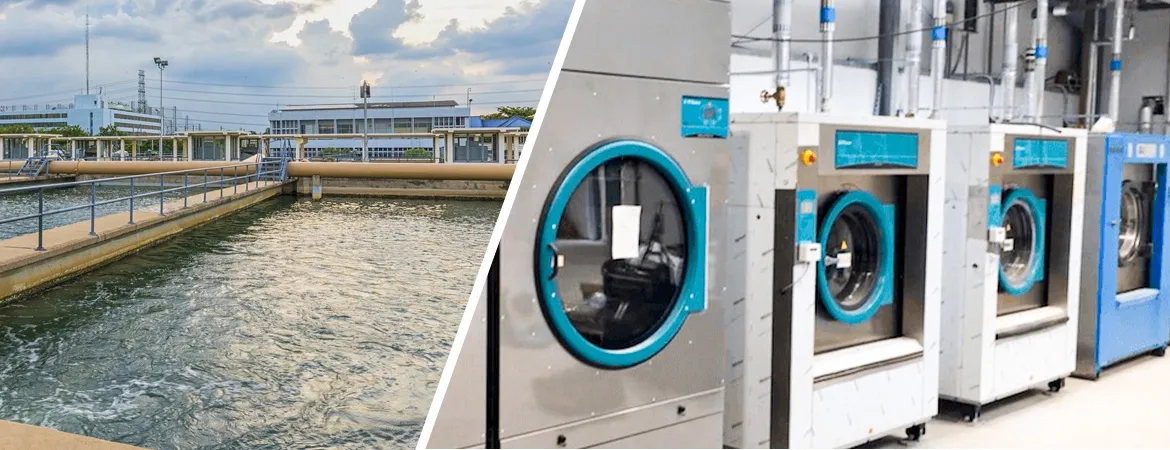

ETP
Plant for Garments Washing/Laundry
Introduction
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) tailored for garments washing and laundry operations are
essential for managing the significant volumes of wastewater generated in the
textile industry. These plants ensure that wastewater is treated effectively to
meet environmental standards before discharge or reuse. Aquafit Technology
provides advanced ETP solutions specifically designed for the unique needs of
the garments washing and laundry sector in Bangladesh.
Definition
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP)
for garments washing and laundry are specialized systems designed to treat
wastewater generated during the cleaning and dyeing of textiles. These plants
use a combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove
contaminants, including dyes, chemicals, and organic matter, from the
wastewater.
How
ETP Plants for Garments Washing/Laundry Work
- Pre-Treatment:
- Screening and
Filtration:
Large solids and debris are removed through screening and filtration
processes.
- Chemical Dosing: Coagulants and
flocculants are added to facilitate the aggregation of fine particles and
impurities, making them easier to remove.
- Primary Treatment:
- Sedimentation: Suspended solids
and particulate matter are settled out in sedimentation tanks, reducing
the load on subsequent treatment stages.
- Secondary
Treatment:
- Biological
Treatment:
Microorganisms break down organic contaminants in aerobic or anaerobic
reactors, such as Activated Sludge Process (ASP) or Moving Bed Biofilm
Reactor (MBBR).
- Advanced
Filtration:
Ultrafiltration (UF) or Reverse Osmosis (RO) may be used for further
purification, removing smaller contaminants and improving water quality.
- Tertiary Treatment:
- Disinfection: Ultraviolet (UV)
light or other disinfection methods are employed to kill any remaining
microorganisms, ensuring the treated water is safe for discharge or
reuse.
- Sludge Management:
- Dewatering and
Disposal:
The sludge generated during the treatment processes is dewatered and
properly disposed of or treated further to minimize environmental impact.
Benefits
of ETP Plants for Garments Washing/Laundry
- Compliance: Ensures that
wastewater meets regulatory standards before discharge, avoiding legal
issues and potential fines.
- Environmental
Protection:
Reduces the release of harmful pollutants and dyes into the environment,
protecting local water bodies and ecosystems.
- Resource
Efficiency:
Treated water can be reused within the facility for various processes,
reducing freshwater consumption and operational costs.
- Operational
Efficiency:
Efficient treatment systems improve the overall sustainability and
operational efficiency of the laundry or garment washing process.
Conclusion
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for garments washing and laundry are vital for managing
wastewater effectively, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, and
promoting sustainability. These plants utilize a combination of physical,
chemical, and biological processes to achieve high-quality treated water.
Aquafit
Technology offers state-of-the-art ETP solutions specifically designed for the
garments washing and laundry industry. Our advanced systems ensure optimal
performance, regulatory compliance, and environmental protection, helping you
achieve efficient and sustainable wastewater management.
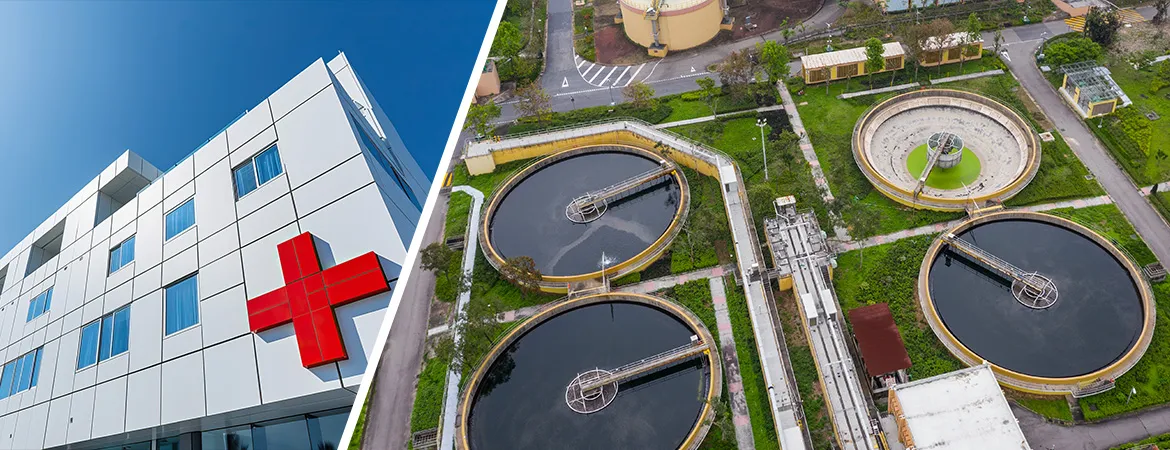

ETP
Plant for Hospitals
Introduction
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for hospitals are crucial in managing the complex and
potentially hazardous wastewater generated by medical facilities. Hospitals
produce wastewater that contains a range of contaminants, including
pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and biological agents, which require specialized
treatment to ensure safe disposal or reuse. Aquafit Technology provides advanced
ETP solutions tailored to the unique needs of healthcare facilities in
Bangladesh.
Definition
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP)
for hospitals are specialized systems designed to treat and manage wastewater
generated from medical and healthcare activities. These plants use a
combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove
contaminants and ensure that treated water meets environmental regulations.
How
ETP Plants for Hospitals Work
- Pre-Treatment:
- Screening and
Filtration:
Initial stages involve removing large solids and debris from the
wastewater through screens and filters.
- Chemical Dosing: Chemicals such as
coagulants and flocculants are added to help aggregate and remove fine
particles and contaminants.
- Primary Treatment:
- Sedimentation: In sedimentation
tanks, suspended solids settle out from the wastewater, reducing the load
on subsequent treatment stages.
- Secondary
Treatment:
- Biological
Treatment:
Microorganisms break down organic matter in aerobic or anaerobic
reactors, such as Activated Sludge Process (ASP) or Moving Bed Biofilm
Reactor (MBBR), effectively treating the wastewater.
- Advanced
Filtration:
Processes such as Ultrafiltration (UF) or Reverse Osmosis (RO) may be
used for further purification, removing smaller contaminants and
improving water quality.
- Tertiary Treatment:
- Disinfection: Ultraviolet (UV)
light or ozone disinfection systems are employed to kill any remaining
pathogens, ensuring that the treated water is safe for discharge or
reuse.
- Special
Considerations:
- Pharmaceuticals
and Chemicals:
Additional treatment steps, such as advanced oxidation processes (AOP) or
activated carbon adsorption, may be required to address pharmaceutical
residues and chemical pollutants.
- Sludge Management: The sludge
generated during treatment is dewatered and properly disposed of or
further treated to minimize environmental impact.
Benefits
of ETP Plants for Hospitals
- Compliance: Ensures that
hospital wastewater meets stringent regulatory standards before discharge,
avoiding legal issues and potential fines.
- Public Health
Protection:
Effectively removes harmful pathogens, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals,
protecting public health and the environment.
- Environmental
Stewardship:
Minimizes the environmental impact of hospital wastewater by reducing
pollutants and ensuring safe disposal or reuse.
- Operational
Efficiency:
Enhances the sustainability and efficiency of hospital operations by
providing a reliable wastewater treatment solution.
Conclusion
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for hospitals are essential for managing the complex and
potentially hazardous wastewater produced by healthcare facilities. By
employing a combination of physical, chemical, and biological treatment
processes, these plants ensure high-quality treated water that meets regulatory
standards.
Aquafit
Technology provides cutting-edge ETP solutions tailored to the specific needs
of hospitals. Our advanced systems ensure optimal performance, regulatory
compliance, and environmental protection, helping you achieve effective and
sustainable wastewater management.
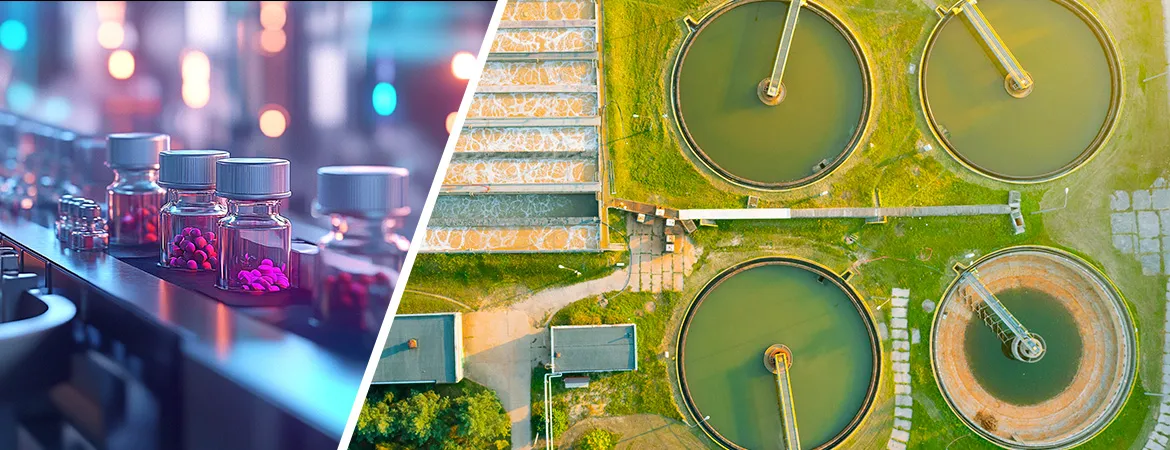

ETP Plant for Pharmaceuticals
Introduction
Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP) tailored for the pharmaceutical industry are essential for managing the complex wastewater generated during pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. The wastewater from pharmaceutical facilities often contains a variety of contaminants, including active pharmaceutical ingredients(APIs), solvents, and other chemicals that require specialized treatment to ensure safe disposal or reuse. Aquafit Technology offers state-of-the-art ETP solutions designed to address the unique challenges of pharmaceutical wastewater in Bangladesh.
Definition
Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP) for pharmaceuticals are specialized systems designed to treat waste water generated by pharmaceutical manufacturing operations. These plants utilize a combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove contaminants and ensure that the treated water meets environmental regulations.
How ETP Plants for Pharmaceuticals Work
- Pre-Treatment:
- Screening and Filtration: Large solids and particulate matter are removed through screening and filtration processes.
- Chemical Dosing: Coagulants and flocculants are added to facilitate the aggregation of fine particles and contaminants, making them easier to remove.
- Primary Treatment:
- Sedimentation: Suspended solids are settled out in sedimentation tanks, reducing the load on subsequent treatment stages.
- Secondary Treatment:
- Biological Treatment: In aerobic or anaerobic reactors, microorganisms break down organic contaminants, including pharmaceuticals, using processes like Activated Sludge Process (ASP) or Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR).
- Advanced Filtration: Technologies such as Ultrafiltration (UF) or Reverse Osmosis (RO) may be employed to further purify the water, removing smaller contaminants and improving water quality.
- Tertiary Treatment:
- Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOP): Techniques such as ozonation or hydrogen peroxide oxidation are used to break down persistent organic contaminants and pharmaceutical residues.
- Disinfection: Ultraviolet (UV) light or ozone disinfection systems ensure that any remaining microorganisms are effectively inactivated.
- Special Considerations:
- Pharmaceutical Residues: Additional treatments may be required to address specific pharmaceutical residues, ensuring they are completely removed.
- Sludge Management: The sludge produced during treatment is dewatered and properly disposed of or further treated to minimize environmental impact.
Benefits of ETP Plants for Pharmaceuticals
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures that pharmaceutical wastewater meets stringent regulatory standards before discharge, avoiding legal issues and potential fines.
- Environmental Protection: Effectively removes hazardous chemicals and pharmaceutical residues, protecting public health and the environment.
- Resource Efficiency: Treats and recycles wastewater efficiently, reducing the demand for fresh water and minimizing operational costs.
- Operational Efficiency: Provides a reliable and sustainable solution for wastewater management, enhancing the overall efficiency of pharmaceutical operations.
Conclusion
Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP) for the pharmaceutical industry are vital for managing the complex and potentially hazardous wastewater generated by pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. By employing a combination of physical, chemical, and biological treatment methods, these plants ensure high-quality treated water that meets regulatory standards.
Aquafit Technology offers advanced ETP solutions specifically designed for pharmaceutical facilities. Our state-of-the-art systems provide optimal performance, regulatory compliance, and environmental protection, helping you achieve effective and sustainable wastewater management.
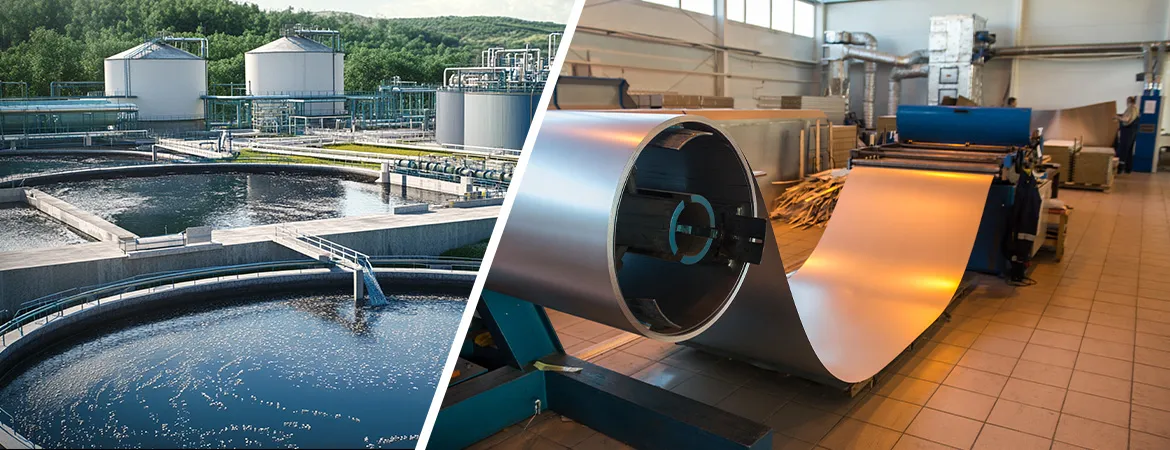

ETP
Plant for Steel Rerolling Mills
Introduction
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) tailored for steel rerolling mills are essential for
managing the substantial volumes of wastewater generated during the steel
manufacturing and rerolling processes. This wastewater often contains heavy
metals, oils, and other contaminants that require specialized treatment to meet
environmental standards and ensure safe disposal or reuse. Aquafit Technology
offers advanced ETP solutions designed to address the unique challenges of
steel rerolling mill wastewater in Bangladesh.
Definition
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP)
for steel rerolling mills are specialized systems designed to treat wastewater
produced from steel manufacturing and rerolling operations. These plants employ
a combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove
contaminants and ensure that the treated water meets environmental regulations.
How
ETP Plants for Steel Rerolling Mills Work
- Pre-Treatment:
- Screening and
Filtration:
Initial stages involve removing large solids and debris from the
wastewater through screening and filtration processes.
- Oil and Grease
Removal:
Coalescers or centrifuges are used to separate and remove oils and
grease, which are commonly present in steel mill wastewater.
- Primary Treatment:
- Sedimentation: In sedimentation
tanks, suspended solids settle out from the wastewater, reducing the load
on subsequent treatment stages.
- Secondary
Treatment:
- Biological
Treatment:
Microorganisms break down organic contaminants in aerobic or anaerobic
reactors, such as Activated Sludge Process (ASP) or Moving Bed Biofilm
Reactor (MBBR). This step helps in treating the organic load and
improving water quality.
- Chemical
Precipitation:
Heavy metals and other pollutants are removed through chemical
precipitation processes, where chemicals are added to form insoluble
compounds that can be separated from the water.
- Tertiary Treatment:
- Advanced
Filtration:
Technologies like Ultrafiltration (UF) or Reverse Osmosis (RO) may be
used for further purification, removing remaining contaminants and
improving water quality.
- Disinfection: Ultraviolet (UV)
light or ozone disinfection systems are employed to kill any remaining
microorganisms and ensure the treated water is safe for discharge or
reuse.
- Sludge Management:
- Dewatering and
Disposal:
The sludge generated during treatment is dewatered and properly disposed
of or further processed to minimize environmental impact.
Benefits
of ETP Plants for Steel Rerolling Mills
- Regulatory
Compliance:
Ensures that steel mill wastewater meets stringent environmental
regulations before discharge, avoiding legal issues and potential fines.
- Environmental
Protection:
Effectively removes heavy metals, oils, and other contaminants, reducing
the impact on local water bodies and ecosystems.
- Resource
Efficiency:
Enables the recycling and reuse of treated water, reducing freshwater
consumption and operational costs.
- Operational
Efficiency:
Provides a reliable and sustainable solution for wastewater management,
enhancing the overall efficiency of steel rerolling mill operations.
Conclusion
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for steel rerolling mills are crucial for managing the
complex and potentially hazardous wastewater generated during steel
manufacturing. By employing a combination of physical, chemical, and biological
treatment processes, these plants ensure high-quality treated water that meets
regulatory standards.
Aquafit
Technology offers state-of-the-art ETP solutions specifically designed for
steel rerolling mills. Our advanced systems ensure optimal performance,
regulatory compliance, and environmental protection, helping you achieve
effective and sustainable wastewater management.
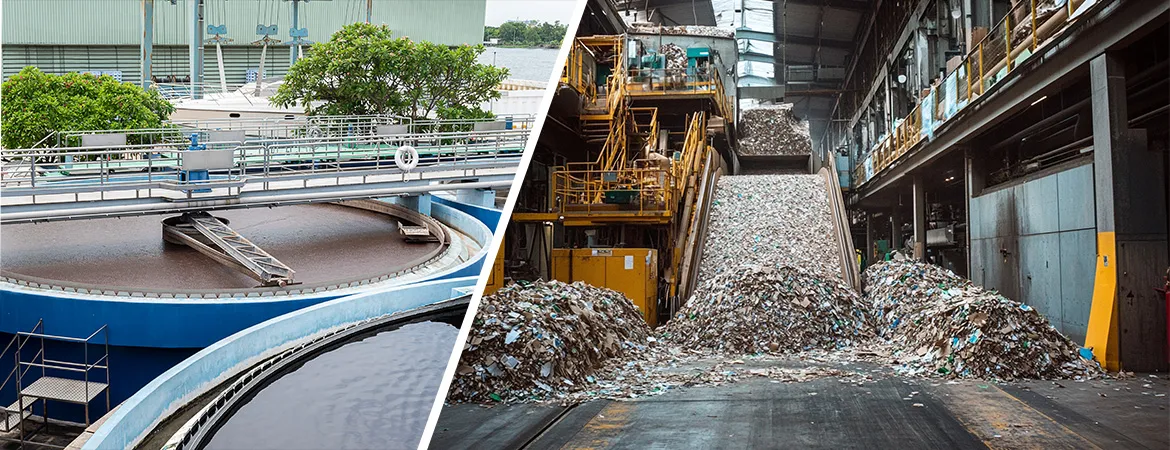

ETP
Plant for Paper Mills: Effective Solutions for Managing Wastewater
Introduction
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for paper mills are crucial for managing the diverse and
often challenging wastewater produced during paper manufacturing. The
wastewater from paper mills contains a variety of contaminants, including
organic matter, chemical additives, and fibers, which require specialized
treatment to ensure environmental compliance and sustainability. Aquafit
Technology provides advanced ETP solutions specifically designed to address the
unique needs of paper mills in Bangladesh.
Definition
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP)
for paper mills are systems engineered to treat wastewater generated during the
paper production process. These plants use a combination of physical, chemical,
and biological processes to remove contaminants and ensure that the treated
water meets environmental standards for discharge or reuse.
How
ETP Plants for Paper Mills Work
- Pre-Treatment:
- Screening and
Filtration:
Large solids, such as paper fibers and debris, are removed through
screening and filtration processes.
- Chemical Dosing: Coagulants and
flocculants are added to help aggregate fine particles and contaminants,
facilitating their removal.
- Primary Treatment:
- Sedimentation: Suspended solids
settle out in sedimentation tanks, reducing the organic and particulate
load on subsequent treatment stages.
- Secondary
Treatment:
- Biological
Treatment:
Microorganisms decompose organic matter in aerobic or anaerobic reactors,
such as Activated Sludge Process (ASP) or Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor
(MBBR). This step is crucial for breaking down biodegradable organic
contaminants.
- Chemical
Precipitation:
Heavy metals and other pollutants are removed through chemical
precipitation, where chemicals form insoluble compounds that can be
separated from the water.
- Tertiary Treatment:
- Advanced
Filtration:
Technologies like Ultrafiltration (UF) or Reverse Osmosis (RO) may be
used for further purification, removing remaining contaminants and
improving water quality.
- Disinfection: Ultraviolet (UV)
light or ozone disinfection systems ensure that any remaining
microorganisms are effectively inactivated, providing safe water for
discharge or reuse.
- Sludge Management:
- Dewatering and
Disposal:
The sludge generated during treatment is dewatered and properly disposed
of or further processed to minimize environmental impact.
Benefits
of ETP Plants for Paper Mills
- Regulatory
Compliance:
Ensures that paper mill wastewater meets stringent environmental
regulations before discharge, avoiding legal issues and potential fines.
- Environmental
Protection:
Effectively removes organic matter, chemical additives, and fibers,
reducing the impact on local water bodies and ecosystems.
- Resource
Efficiency:
Facilitates the recycling and reuse of treated water, reducing freshwater
consumption and operational costs.
- Operational
Efficiency:
Provides a reliable and sustainable solution for wastewater management,
enhancing the overall efficiency of paper mill operations.
Conclusion
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for paper mills are essential for managing the diverse
and often complex wastewater generated during paper manufacturing. By utilizing
a combination of physical, chemical, and biological treatment processes, these
plants ensure high-quality treated water that meets regulatory standards.
Aquafit
Technology offers state-of-the-art ETP solutions tailored for paper mills. Our
advanced systems ensure optimal performance, regulatory compliance, and
environmental protection, helping you achieve effective and sustainable
wastewater management.
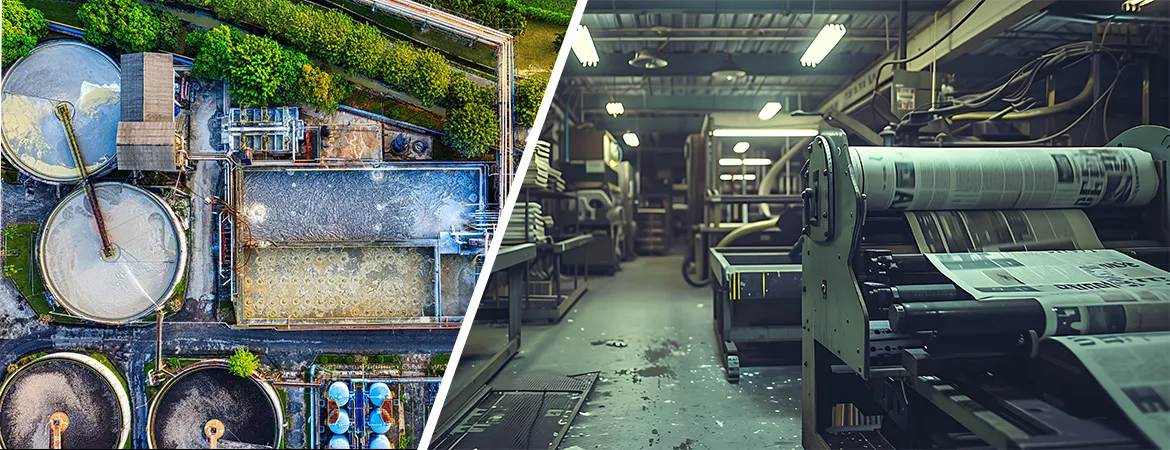

ETP
Plant for Printing and Press
Introduction
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for printing and press industries are essential for
managing the diverse and often challenging wastewater generated from printing
processes. This wastewater typically contains inks, solvents, and various
chemical additives that require specialized treatment to ensure environmental
compliance and sustainability. Aquafit Technology provides advanced ETP
solutions tailored to the unique needs of printing and press facilities in
Bangladesh.
Definition
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP)
for printing and press industries are designed to treat wastewater produced
during printing and press operations. These plants utilize a combination of
physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove contaminants and ensure
that the treated water meets environmental standards for discharge or reuse.
How
ETP Plants for Printing and Press Work
- Pre-Treatment:
- Screening and
Filtration:
Large solids, such as paper fibers and debris, are removed through
screening and filtration processes.
- Oil and Grease
Removal:
Coalescers or separators are used to remove oils, greases, and solvents
commonly found in printing wastewater.
- Primary Treatment:
- Sedimentation: Suspended solids
settle out in sedimentation tanks, reducing the load on subsequent
treatment stages and removing larger particles.
- Secondary
Treatment:
- Biological
Treatment:
In aerobic or anaerobic reactors, microorganisms decompose organic
contaminants, including residual inks and chemicals, using processes like
Activated Sludge Process (ASP) or Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR).
- Chemical
Precipitation:
Heavy metals and other pollutants are removed through chemical
precipitation, where chemicals are added to form insoluble compounds that
can be separated from the water.
- Tertiary Treatment:
- Advanced
Filtration:
Technologies such as Ultrafiltration (UF) or Reverse Osmosis (RO) may be
used to further purify the water, removing any remaining contaminants and
improving water quality.
- Disinfection: Ultraviolet (UV)
light or ozone disinfection systems ensure that any remaining
microorganisms are effectively inactivated, providing safe water for
discharge or reuse.
- Special
Considerations:
- Ink Residues: Additional
treatments, such as advanced oxidation processes (AOP) or activated
carbon adsorption, may be necessary to address specific ink residues and
chemical pollutants.
- Sludge Management: The sludge
generated during treatment is dewatered and properly disposed of or
further processed to minimize environmental impact.
Benefits
of ETP Plants for Printing and Press
- Regulatory
Compliance:
Ensures that wastewater from printing and press operations meets stringent
environmental regulations before discharge, avoiding legal issues and
potential fines.
- Environmental
Protection:
Effectively removes inks, solvents, and other contaminants, reducing the
impact on local water bodies and ecosystems.
- Resource
Efficiency:
Facilitates the recycling and reuse of treated water, reducing freshwater
consumption and operational costs.
- Operational
Efficiency:
Provides a reliable and sustainable solution for wastewater management,
enhancing the overall efficiency of printing and press operations.
Conclusion
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for printing and press industries are vital for managing
the diverse and potentially hazardous wastewater generated during printing
processes. By employing a combination of physical, chemical, and biological
treatment processes, these plants ensure high-quality treated water that meets
regulatory standards.
Aquafit
Technology offers state-of-the-art ETP solutions specifically designed for the
printing and press industry. Our advanced systems ensure optimal performance,
regulatory compliance, and environmental protection, helping you achieve
effective and sustainable wastewater management.
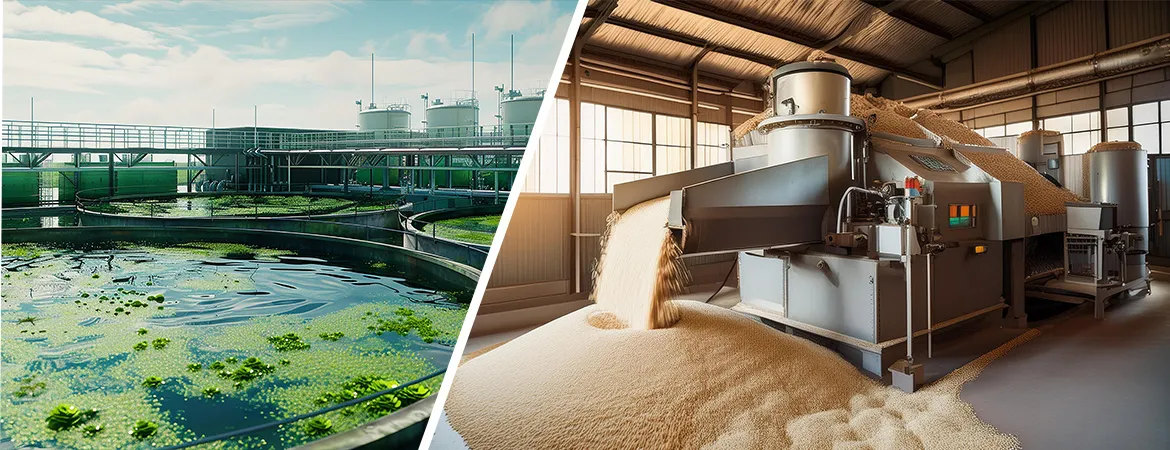

ETP
Plant for Auto Rice Mills
Introduction
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for auto rice mills are crucial for managing the
wastewater generated during rice milling processes. This wastewater often
contains organic matter, starch, and other contaminants that require
specialized treatment to ensure environmental compliance and sustainability.
Aquafit Technology provides advanced ETP solutions specifically designed to
address the unique needs of auto rice mills in Bangladesh.
Definition
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP)
for auto rice mills are systems designed to treat wastewater produced during
rice milling operations. These plants utilize a combination of physical,
chemical, and biological processes to remove contaminants and ensure that the
treated water meets environmental standards for discharge or reuse.
How
ETP Plants for Auto Rice Mills Work
- Pre-Treatment:
- Screening and
Filtration:
Initial stages involve removing large solids and debris, such as husks
and fibers, through screening and filtration processes.
- Oil and Grease
Removal:
Coalescers or separators may be used to remove oils and greases from the
wastewater.
- Primary Treatment:
- Sedimentation: Suspended solids,
including rice bran and starch, settle out in sedimentation tanks. This
step reduces the load on subsequent treatment stages by removing larger
particles.
- Secondary
Treatment:
- Biological
Treatment:
Microorganisms decompose organic matter in aerobic or anaerobic reactors,
such as Activated Sludge Process (ASP) or Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor
(MBBR). This step is crucial for breaking down biodegradable organic
contaminants.
- Chemical
Precipitation:
Additional treatment may involve adding chemicals to precipitate heavy
metals and other pollutants that may be present in the wastewater.
- Tertiary Treatment:
- Advanced
Filtration:
Technologies like Ultrafiltration (UF) or Reverse Osmosis (RO) may be
used for further purification, removing any remaining contaminants and
improving water quality.
- Disinfection: Ultraviolet (UV)
light or ozone disinfection systems are employed to ensure that any
remaining microorganisms are effectively inactivated, providing safe
water for discharge or reuse.
- Sludge Management:
- Dewatering and
Disposal:
The sludge generated during treatment is dewatered and properly disposed
of or further processed to minimize environmental impact.
Benefits
of ETP Plants for Auto Rice Mills
- Regulatory
Compliance:
Ensures that wastewater from auto rice mills meets stringent environmental
regulations before discharge, avoiding legal issues and potential fines.
- Environmental
Protection:
Effectively removes organic matter, starch, and other contaminants,
reducing the impact on local water bodies and ecosystems.
- Resource
Efficiency:
Enables the recycling and reuse of treated water, reducing freshwater
consumption and operational costs.
- Operational
Efficiency:
Provides a reliable and sustainable solution for wastewater management,
enhancing the overall efficiency of rice milling operations.
Conclusion
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for auto rice mills are essential for managing the
wastewater generated during rice milling processes. By utilizing a combination
of physical, chemical, and biological treatment methods, these plants ensure
high-quality treated water that meets regulatory standards.
Aquafit
Technology offers cutting-edge ETP solutions tailored for auto rice mills. Our
advanced systems provide optimal performance, regulatory compliance, and
environmental protection, helping you achieve effective and sustainable
wastewater management.
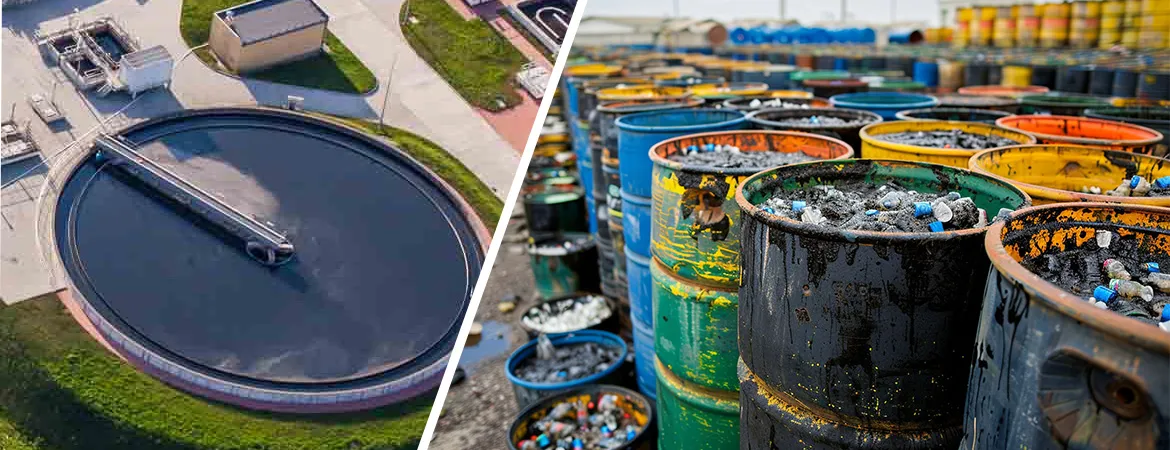

ETP
Plant for Oil and Grease Waste
Introduction
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for oil and grease waste are essential for managing the
complex wastewater generated from industries such as food processing,
automotive, and manufacturing. Oil and grease waste poses significant
challenges due to its high pollutant load and potential environmental impact.
Aquafit Technology provides advanced ETP solutions specifically designed to
address these challenges and ensure effective treatment of oil and grease
waste.
Definition
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP)
for oil and grease waste are specialized systems designed to treat wastewater
containing high concentrations of oils, greases, and other contaminants. These
plants use a combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes to
remove pollutants and ensure that the treated water meets environmental
discharge standards.
How
ETP Plants for Oil and Grease Waste Work
- Pre-Treatment:
- Screening and
Filtration:
Large solids and debris, such as sludge and particulate matter, are
removed through screening and filtration processes.
- Oil-Water
Separation:
Coalescers or gravity separators are used to separate and remove oils and
greases from the wastewater. This step is crucial for reducing the load
on subsequent treatment stages.
- Primary Treatment:
- Sedimentation: In sedimentation
tanks, suspended solids and remaining oil droplets settle out, further
reducing the pollutant load and improving the efficiency of secondary
treatment.
- Secondary
Treatment:
- Biological
Treatment:
In aerobic or anaerobic reactors, microorganisms decompose remaining
organic contaminants. Processes like Activated Sludge Process (ASP) or
Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) help break down biodegradable oils and
greases.
- Chemical Dosing: Coagulants and
flocculants may be added to aid in the removal of fine particles and
emulsified oils, facilitating their separation from the water.
- Tertiary Treatment:
- Advanced
Filtration:
Technologies such as Ultrafiltration (UF) or Reverse Osmosis (RO) may be
employed for further purification, removing any remaining contaminants
and ensuring high-quality treated water.
- Disinfection: Ultraviolet (UV)
light or ozone disinfection systems are used to eliminate any remaining
microorganisms and ensure that the treated water is safe for discharge or
reuse.
- Sludge Management:
- Dewatering and
Disposal:
The sludge generated during treatment is dewatered and properly disposed
of or further processed to minimize environmental impact.
Benefits
of ETP Plants for Oil and Grease Waste
- Regulatory
Compliance:
Ensures that wastewater containing oils and greases meets environmental
regulations before discharge, avoiding legal issues and potential fines.
- Environmental
Protection:
Effectively removes oils, greases, and other contaminants, reducing the
impact on local water bodies and ecosystems.
- Resource
Efficiency:
Facilitates the recycling and reuse of treated water, reducing freshwater
consumption and operational costs.
- Operational
Efficiency:
Provides a reliable and sustainable solution for wastewater management,
enhancing the overall efficiency of industrial operations.
Conclusion
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for oil and grease waste are vital for managing
wastewater with high concentrations of oils and greases. By employing a
combination of physical, chemical, and biological treatment processes, these plants
ensure that the treated water meets regulatory standards and minimizes
environmental impact.
Aquafit
Technology offers cutting-edge ETP solutions designed specifically for handling
oil and grease waste. Our advanced systems provide optimal performance,
regulatory compliance, and environmental protection, helping you achieve
effective and sustainable wastewater management.
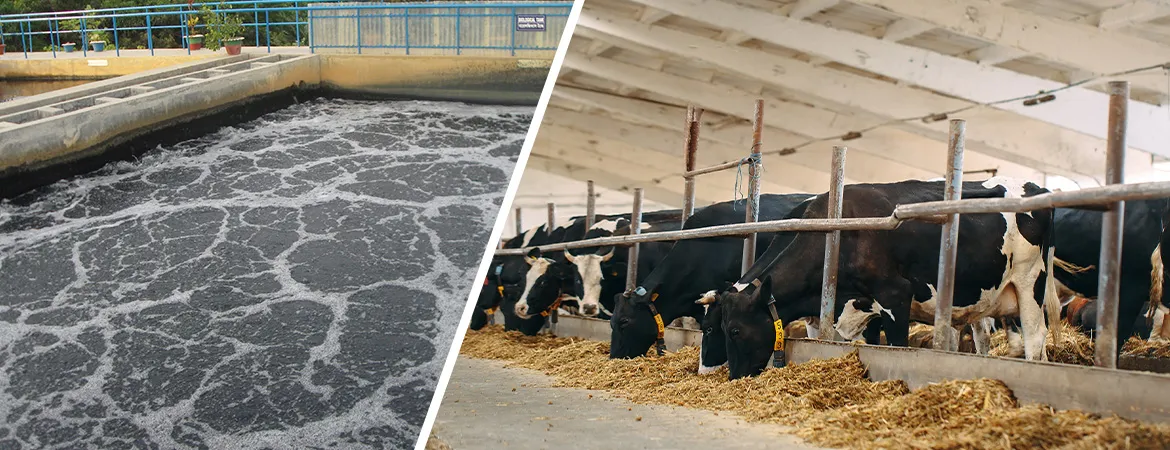

ETP
Plant for Dairy Farms and Cattle Houses
Introduction
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for dairy farms and cattle houses play a crucial role in
managing the substantial volumes of wastewater generated from dairy and
livestock operations. This wastewater often contains high levels of organic
matter, nutrients, and other contaminants that require effective treatment to
ensure environmental compliance and sustainability. Aquafit Technology provides
advanced ETP solutions tailored to the unique needs of dairy farms and cattle
houses in Bangladesh.
Definition
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP)
for dairy farms and cattle houses are specialized systems designed to treat
wastewater produced from dairy and livestock operations. These plants utilize a
combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove
contaminants and ensure that the treated water meets environmental discharge
standards.
How
ETP Plants for Dairy Farms and Cattle Houses Work
- Pre-Treatment:
- Screening and
Filtration:
Large solids such as manure, straw, and feed residues are removed through
screening and filtration processes.
- Settling Tanks: Initial settling
tanks help to separate larger solids from the wastewater, reducing the
load on subsequent treatment stages.
- Primary Treatment:
- Sedimentation: In sedimentation
tanks, suspended solids and heavier particles settle out. This step helps
reduce the organic and particulate load on secondary treatment processes.
- Secondary
Treatment:
- Biological
Treatment:
Microorganisms decompose organic contaminants in aerobic or anaerobic
reactors. Processes like Activated Sludge Process (ASP) or Moving Bed
Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) are used to treat the high organic load and
nutrients present in dairy and cattle wastewater.
- Nutrient Removal: Specialized
processes, such as nitrification-denitrification, are used to remove
excess nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, which can cause
environmental issues if discharged untreated.
- Tertiary Treatment:
- Advanced
Filtration:
Technologies such as Ultrafiltration (UF) or Reverse Osmosis (RO) can be
employed for further purification, removing remaining contaminants and
ensuring high-quality treated water.
- Disinfection: Ultraviolet (UV)
light or ozone disinfection systems are used to ensure that any remaining
microorganisms are effectively inactivated, providing safe water for
discharge or reuse.
- Sludge Management:
- Dewatering and
Disposal:
The sludge generated during treatment is dewatered and properly disposed
of or further processed to reduce its volume and minimize environmental
impact.
Benefits
of ETP Plants for Dairy Farms and Cattle Houses
- Regulatory
Compliance:
Ensures that wastewater from dairy farms and cattle houses meets
environmental regulations before discharge, avoiding legal issues and
potential fines.
- Environmental
Protection:
Effectively removes organic matter, nutrients, and other contaminants,
reducing the impact on local water bodies and ecosystems.
- Resource
Efficiency:
Facilitates the recycling and reuse of treated water, reducing freshwater
consumption and operational costs.
- Operational
Efficiency:
Provides a reliable and sustainable solution for wastewater management,
enhancing the overall efficiency of dairy and livestock operations.
Conclusion
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for dairy farms and cattle houses are essential for
managing the complex wastewater generated from these operations. By employing a
combination of physical, chemical, and biological treatment methods, these
plants ensure high-quality treated water that meets regulatory standards and
minimizes environmental impact.
Aquafit
Technology offers state-of-the-art ETP solutions specifically designed for
dairy farms and cattle houses. Our advanced systems ensure optimal performance,
regulatory compliance, and environmental protection, helping you achieve
effective and sustainable wastewater management.
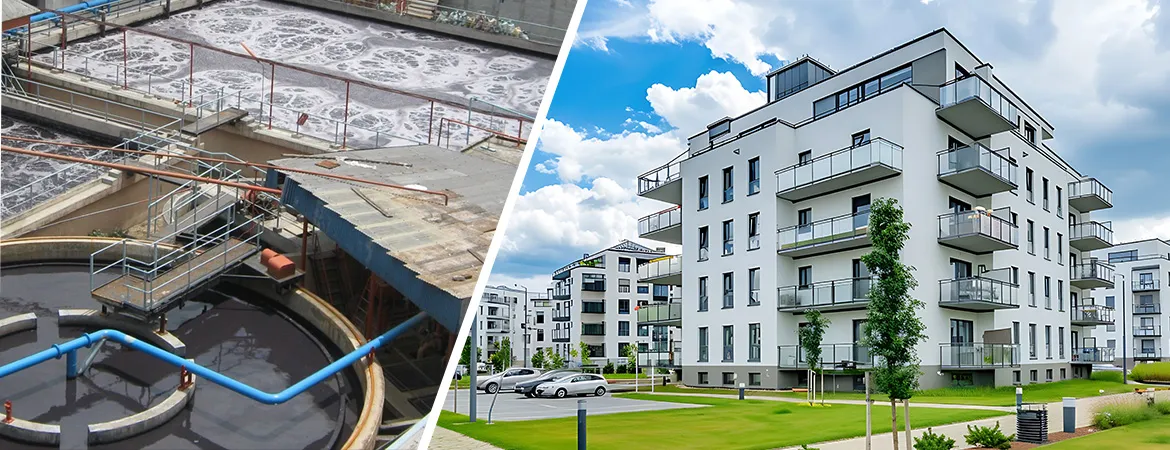

ETP
Plant for Apartment Wastewater
Introduction
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for apartment wastewater are essential for managing the
wastewater generated from residential buildings. With the increasing density of
urban areas, managing wastewater effectively has become a critical aspect of
sustainable living. Aquafit Technology provides advanced ETP solutions designed
to address the unique challenges of treating wastewater from apartment
complexes in Bangladesh.
Definition
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP)
for apartment wastewater are systems designed to treat the wastewater produced
by residential buildings. These plants use a combination of physical, chemical,
and biological processes to remove contaminants and ensure that the treated
water meets environmental standards for discharge or reuse.
How
ETP Plants for Apartment Wastewater Work
- Pre-Treatment:
- Screening and
Filtration:
Large solids, such as paper, plastics, and other debris, are removed
through screening and filtration processes.
- Grease Traps: Grease and oils
from kitchen wastewater are captured in grease traps to prevent them from
interfering with the treatment process.
- Primary Treatment:
- Sedimentation: In primary
sedimentation tanks, suspended solids settle out, reducing the load on
subsequent treatment stages and removing larger particles from the
wastewater.
- Secondary
Treatment:
- Biological
Treatment:
Microorganisms break down organic contaminants in aerobic or anaerobic
reactors. Common processes include Activated Sludge Process (ASP) or
Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR), which treat the organic load and
ensure effective decomposition of pollutants.
- Nutrient Removal: Techniques like
nitrification-denitrification may be employed to remove excess nutrients
such as nitrogen and phosphorus, which can contribute to environmental
pollution if not adequately treated.
- Tertiary Treatment:
- Advanced
Filtration:
Technologies such as Ultrafiltration (UF) or Reverse Osmosis (RO) are
used for further purification, removing any remaining contaminants and
ensuring high-quality treated water.
- Disinfection: Ultraviolet (UV)
light or ozone disinfection systems are used to ensure that any remaining
microorganisms are effectively inactivated, providing safe water for
discharge or potential reuse.
- Sludge Management:
- Dewatering and
Disposal:
The sludge generated during treatment is dewatered and either disposed of
or processed further to reduce its volume and environmental impact.
Benefits
of ETP Plants for Apartment Wastewater
- Regulatory
Compliance:
Ensures that wastewater from apartment complexes meets stringent
environmental regulations before discharge, avoiding legal issues and
potential fines.
- Environmental
Protection:
Effectively removes organic matter, nutrients, and contaminants, reducing
the impact on local water bodies and ecosystems.
- Resource
Efficiency:
Facilitates the recycling and reuse of treated water, which can be used
for non-potable purposes such as irrigation, reducing freshwater
consumption and operational costs.
- Operational
Efficiency:
Provides a reliable and sustainable solution for managing residential
wastewater, enhancing the overall efficiency of apartment complexes.
Conclusion
Effluent
Treatment Plants (ETP) for apartment wastewater are crucial for managing the
diverse and potentially challenging wastewater generated from residential
buildings. By employing a combination of physical, chemical, and biological
treatment processes, these plants ensure high-quality treated water that meets
regulatory standards and minimizes environmental impact.
Aquafit
Technology offers advanced ETP solutions specifically designed for apartment
complexes. Our state-of-the-art systems provide optimal performance, regulatory
compliance, and environmental protection, helping you achieve effective and
sustainable wastewater management for residential buildings.